Terms system and control volume turns out to be quite familiar to each other when you study thermodynamics. The word system is referred to any fixed mass that comes along with a boundary. Though, along with time the body of any system may change, but you might be sure that their mass would remain the same.
You will find the same thing in this piston cylinder arrangement that is shown in diagram. Think that gas is filled in cylinder that comes with closed option by piston which is found at right hand end. Gas is said to be the system. In case piston is operated by pushing, the gas might get compressed.
The boundary of system may move. But mass would not move out of boundary as the system comes with fixed mass. It is quite simple to analyze system in case of piston cylinder arrangement. But, the question remains whether all systems are simple. The answer is “no”. In regard to fluid dynamics, systems are far more complicated. You can take flow about plane for example.
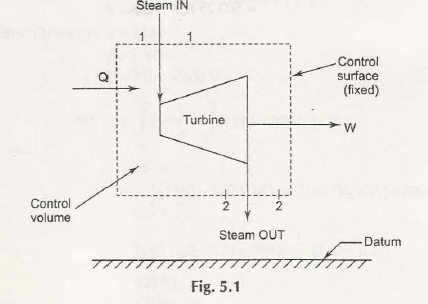
The other method available is control volume approach. Though, in this case we do not put emphasize on fixed mass of fluid. Rather it is necessary to establish a window for observation in flow. This is what is called control volume. A control volume may come along with fixed boundary.
Mass, energy and momentum are found to cross the boundary. It becomes important to perform balance of mass, energy and momentum that would transfer from different boundary which may deduce any changes and can affect the properties of flow that may happen within control volume.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction to statics
- Introduction to vector algebra
- Two dimensional force systems
- Introduction concept of equilibrium of rigid body
- Friction introduction
- Introduction about distributed forces
- Area moments of inertia in rectangular and polar coordinates
- Mass moment of inertia introduction
- Work done by force
- Kinematics of particles
- Position vector velocity and acceleration
- Plane kinematics of rigid bodies introduction
- Combined motion of translation and rotation
- Rectilinear motion in kinetics of particles
- Work and energy
- Linear momentum
- Force mass acceleration
- Simple stress introduction
- Normal strain
- Statically indeterminate system
- Introduction to thermodynamics
- Statement of zeroth law of thermodynamics with explanation
- Heat and work introduction
- First law of thermodynamics for a control mass closed system undergoing a cycle
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-