Decision Taken
When a record breaking blizzard hit the entire east coast and threatened to bring transportation to a halt with inches of snow piling up in airports, American Airlines employee Danny Burgin out of Fort Worth was to deal with the life and safety of thousands of passengers and flights. Although blizzards are fairly predictable and make it possible for cleanup and disaster relief services to work around the apex point, any decision taken will not be an easy one because lives are at stake here. At any organizational level, decisions are the essence of managerial duties.
Everyone in a company has to manage something. Whether it is the board of directors of an organization, or the branch manager and supervisor, everyone has to decide on matters that will affect their colleagues and subordinates. The complexity and severity of the decisions to be made depends on the hierarchy of the manager. A CEO or a GM decides about organizational goals, avenues to pursue, and investment opportunities; whereas a project manager decides about pay raises, quality control, employee discipline and satisfaction etc. So how do they do it?
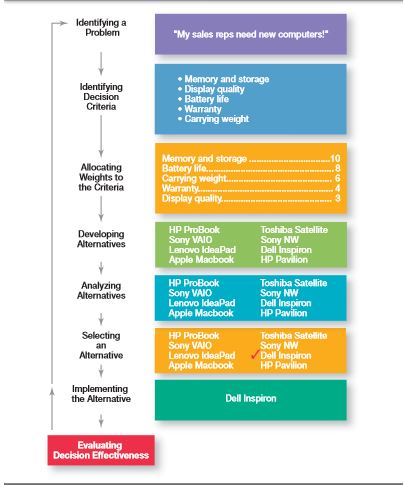
Although decision is essentially a choice amongst more than two alternatives, reaching a conclusion is an entire process, comprised of critical thinking and shrewd judgment; not just picking out random alternatives out of all available options. Just think about the time you spend before deciding on what to have for lunch. Did you already have something in mind, or did you think about all your available choices and then decide? The principles of management are ingratiated into every aspect of our daily life. So how does one find an answer? According to research, there are a few basic steps a manager, or everyone else covers while making any decision. Let us consider a scenario where the manager is deciding on the kind of laptops to be bought for office.
 Step 1: Know what the problem is
Step 1: Know what the problem is
Every decision made has to be reviewed after a certain period of time due to various factors leading it to obsoletion. Any decision is made with a goal of solving a problem. Recognizing the problem is a big part of a manager’s job. However, problems usually present themselves in various symptoms observable around the periphery of the problem zone. It is very pragmatic to be able to distinguish between problems and the symptoms arising from them. For instance, Amanda found out about the need to buy new laptops after her reps complained about it. Recognition of the problem is as important as is execution of the correct alternatives. Sometimes a problem is less obvious, and it is necessary to focus on the telltale signs to be better equipped. Identifying problems depends largely on the perception and intuition of the manager. Problem detection is largely subjective, which make it a human skill, where some are better at it than other, with no exact science governing any of it.
Step 2: What are the constraints of a decision?
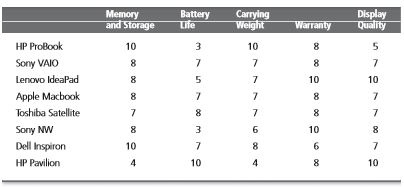
Every decision is bound in its stringent conditions, which has to be taken into careful consideration for choosing the best alternative. In our chosen scenario, she would have to decide on which features to look for in the laptops she wishes to buy. After more research about her impending decision, she chooses to filter her choices based on these.
Step 3: How feasible are the alternatives?
In order to rank the deciding criteria according to their importance, mark the most important criteria according to you as any number. The other criteria can be rated with respect to that. This helps in prioritizing the various constraints and easing the process of deciding.
Step 4: Deducing with different alternatives to tackle the problem
Any situation can be managed in different ways. It is a manager’s job to provide the suitable alternative approaches in order to solve the problem. Evaluation of the alternatives comes later. The type and methodology of these alternatives vary greatly from people to people, depending on their creativity, shrewdness, and worldview.
Step 5: Review of analysis of given alternatives
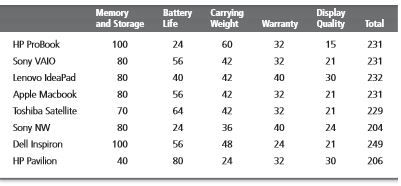
Analysis involves careful consideration of all the provided alternatives with respect to the constraints defined in step 2. This can be done my weighted average method i.e., an arbitrary value is assigned to every constraint and the corresponding coefficient of each alternative is multiplied to it and cumulated. If one of those alternatives seems to be clear ahead on all aspects by simple observation, then it is chosen. Amanda has assigned constants to all the boundary conditions and has come up with the weighted alternatives.
 Step 6: Choosing an approach
Step 6: Choosing an approach
After detailed consideration and analysis of the given alternatives, the manager must choose one of them, preferably the one which gives the highest cumulative amount in step 5. Most managers would choose would prefer this option, whereas there are some others who might think with their gut and reach a different conclusion.
Step 7: Implementation of the chosen alternative
Once the alternative is chosen and the course of action determined, it is implemented. In oversight, constant monitoring and feedback from the people affected by it should be taken under advisement for further amendment and long-term strategizing. An interactive atmosphere encourages acceptance of the alternative much faster and makes implementation and amendment more streamlined. A manager has to keep track of the general reaction of his employees towards the implemented decision.
Step 8: Assessment of effectiveness of implemented decision
If the problem still persists after the decision has been made, the manager has to modify any of the above steps; or even start from square one, and reanalyze the data given and make another decision. Effective implementation, proper evaluation of alternatives, and incorrect definition of problem conditions can lead to the failure of an implemented decision. The manager has to make astute observations, careful considerations and ensure wholesale acceptance of the decision to ensure its effectiveness.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- management and organizations a managers dilemma
- Understanding managements context constraints and challenges
- Managing in a global environment
- Managing diversity
- What is social responsibility
- Managing change and innovation
Links of Next Fundamentals of Management Topics:-
- How is a decision taken
- How is a decision made
- Classification of decisions and decision making conditions
- Styles of decision making
- How to make and implement decisions effectively
- Case application 1 curtain fall
- Case application 2 tumultuous waters
- Summing up decision making managers job
- Check out your managerial instincts
- Foundations of planning
- Strategic management
- Basic organizational design
- Adaptive organizational design
- Managing human resources
- Managing teams
- Understanding individual behavior