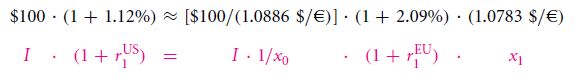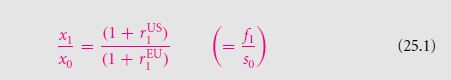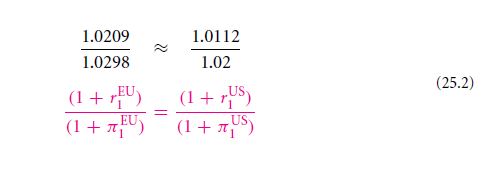You should know that the market of finance in the USA is the biggest in the entire world. You will be surprised to learn that nearly 50% of the capital of the stock as well as bond market is located in the US. The Europe would have one fourth and Japan one-eighth of the rest of the market. In the coming times, it can be predicted that countries from South East Asia especially China will play a much bigger role in the market. The event of taking place of corporate borrowing is still more tilted in the favor of USA corporations. In fact the USA based companies actually hold 75% of the bond issues made, of corporate type.
Going through the whole chapter, you will understand that the authors want to view the USA as a wide collection of other countries. In order to bring in reference of all those nations having capital markets which are open in nature, they would simply be called the OECD states. The full form of OECD is Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. This organization has members in form of lots of European as well as countries of the North, Australia, Japna as well as Korea among Asian countries. The rate of currency exchange, is the biggest difference prevailing in the transactions taking place within USA and some other country, part of the OECD. Hence the exchange rates can be regarded as the first edict of business.
25.1 A Exchange Rates and Currency-Dependent Rates of Return
The exchange rate for the money is the cost involved in one unit of currency of any country when equated with one unit of currency of the other country. This kind of system is no different from the price of a particular good in a store. For example in the store of a grocer a particular item can go for a certain amount for a certain number of items. The amount would vary is the number of goods is varied. The monetary conventions are standardized in nature. The exchange rate of the dollar-pound or the dollar-Yen actually remains constant. One currency will decrease in value when the exchange rate decreases. A dollar can depreciate when the exchange rate with Yen decreases, whereas the converse is true for the Euro.
Convention: Yen/U.S. dollar but U.S. dollar/euro and U.S.dollar/British pound.
Financial exchange rates are nearly free of friction friction less without involvement of physical cash.
On course of your travels to different places, the exchange rates that you give off are not quite comforting in nature. These exchanges usually take place from the booths present in hotel lobbies or lounge in the airport, mostly for the travelling tourists. The currency used in financial transactions, has a certain market too. The exchange rates of here will be applied to the biggest of the transactions. Most of these transactions are liquidated in nature in some of the fiercest markets of the world. The costs involved with transactions are also very less in here too. Not much concrete statistics are available regarding the trading in currencies. Usually the trading is round about 1.5 trillion dollars per day.in order to get a fair idea of this, you should know that this amount is 10 times the trading volume taking place in equities. It is also nearly 10% of the US GDP annually. In this type of active market of finance, you can really expect some amount of efficiency. You have to realize that no investor possess the ability to foresee the different rates of exchange, the market will always remain the best predictor.
25.1 B Currency Forwards and Interest Rate Parity
You will see that various companies will be able to get around the risks which occur owing to fluctuation of exchange rate. The best known contract will always be the spot contract. This actually happens owing to currency exchange and lasts a short duration of time based on the exchange rate.
Forwards versus Futures
Different transactions of ten take place right on the spot, as a trader you can also engage in transactions which are quoted according to the spot rates for the future. When a forward contract is signed, an agreement is reached where the people pledge to get certain sums of money exchanged at a rate which is prevalent during the time of agreement. The structuring of these contracts are such, that the exchange always remain fair between the two parties. In an agreement for example people can pledge to exchange 1.5 million dollars for 1 million dollars in the future.
A forward contract can be defined as contract for exchanging of currency in the near future.
Similar to many different assets, the currencies too get involved in trade as forward contracts as well as futures contracts. A future contract differs from the forward one in the fact that the value of contract can change every day. You may have purchased a contract of 100 dollars, which would provide you with a return value of 200 dollars. However the value of the currency itself will determine how much you will get in return, hence if the value of the dollar currency increases then you will get a higher sum in return. Most of the future based contracts require settlement on a short term basis. Hence the seller can pay you the amount at the end of the same day of making the contract. After particular settlement is completed, the value of contract becomes zero again; the same is not possible in forward contract.
This type of quick settlement actually causes a reduction in the credit risk for the different parties. Hence the possibility of a party to lose big amounts decreases and hence the contract is not defaulted upon. The concept of futures settlement has been there for quite some time now. The security exchanges in Holland had these features right from the 1600s. You will realize that avoiding defaulting is a really healthy practice. Different future exchanges nowadays take place in the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. The currency exchange rates for the future will hence be available easily on searching them online or better still.
Unlike forwards contracts, futures are settled on a daily basis.
Futures contracts possess the benefit that it is never worth skipping town for either of the two parties.
Forwards can be termed as contracts linking one party to another.
The forward dealings take place in markets which can be termed as over the counter ones. In these markets you will not come across a forward rate which is different from the others. The different companies which are interested in the dealings would ring up the banks and they would convey the forward rates to these people. Different factors will be taken into account by the banks such as the credit history of the company as well as who is present at the other end of the line. Hence the forward rates differ slightly from one bank to another. The market for the forward deals is quite vast in comparison to the futures.
You are going to find subtle differences in the prices of the forwards and futures. For example a particular currency might stand at 5 units at a particular period and the forward at 5.25 and the futures at 5.30 units respectively. These 0.05 units of difference was caused due to various factors such as credit risks of individuals as well as disputes occurring as to which person would receive the cash during the intermediate period, receipts would be generated accordingly too. For traders who deal in currencies the difference in price existing between a future and forward can matter to a certain extent. However when illustrating finance of the corporate world, these small differences can be ignored and they can be treated as one.
The price difference existing between the future and forward contract is negligible in amount.
Covered IRP can be termed as a round-trip contract, which has the ability to fixate the forward rate of currency base upon the spot rate as well as two interest rates.
Covered Interest Rate Parity
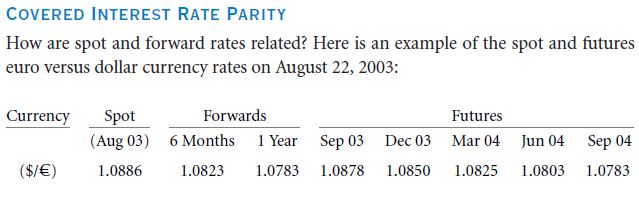
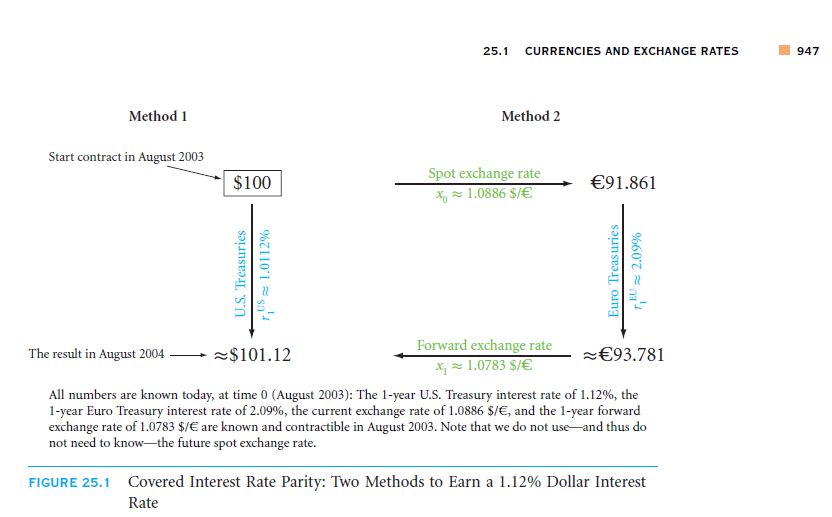
You have the option of getting 1.0886 dollars on the spot in exchange of a euro or getting it exchanged in the future, say an year later for 1.0783 dollars or even less than that. You will ask the question whether the Euro’s value would decrease in comparison to the dollar, it may, but usually it will not. There exists the condition of Interest Rate Parity, which links the spot rate of currencies with the forward rate as well as the treasury rates of the governments. Actually here it is assumed that the futures price is the forward price. The figure above will demonstrate the IRP by use of two different methods which will ultimately produce the same result. Viewing the date, 22 August, 2003, the treasury rate of interest of the dollar was found to be 1.12%. The interest rates in the banks of Europe were seen to be 2.09%. Different currencies have different curves of yield. You will be able to find these on websites. In the above figure, the left hand side shows how you were able to save your 100 dollars and receive 101.12 dollars a year later. The figure on the right will show how you could have changed 100 dollars into 91.861 euros by depositing them in the banks of Europe. The 101.12 dollars are actually equivalent to 93.781 euros. This forward exchange rate will be kept constant for a year after your investment. Hence it will be impossible for you to receive any amount which has not already been decided upon.
If you are wondering what would happen in the forward exchange rate would have changed for the year. In such scenarios, you would require changing the dollars into euros presently and put a lock upon the rate of exchange of euros in future. In this manner the euros are converted back into dollars but you get the interest rate in European money. The 100 dollars could be exchanged for 91.861 euros and thus you would have got 93.781 euros along with a lock on the exchange rate for the reverse currency, after spending a net 93.781 euros. Hence this amount is nearly 1 dollar more than the amount you would have received by investing in the US. Hence in this case the treasury of the US can be deemed as inferior in nature.
If there was absence of transaction costs along with IRP, you could become rich easily
ANECDOTE
Currency Arbitrage in the middle Ages
The concept of currency arbitrage is not at all new in the market. In the 1200s, the bankers from Venice gambled in the different currencies on a very big scale. Two times per year, ships from there would visit the Middle East carrying silver in them while on return the ships would be filled with gold. The rate of exchange of the gold was different from that of silver in the Middle East countries than that in Europe. The gold arrived in Middle East through the hands of Mongols from China. Within two centuries it was seen that the Venetians had changed the standard of gold in the East with silver from the West and vice versa in the West. Hence the reserves of the Venetian bankers grew larger in size and cashless transactions got introduced for merchants along with supplying them with lines of credit. However by the next century, the occurrence of Black Death in Europe along with massive defaulters the bankers of Venice suffered and there emerged the bankers of Germany, the Fuggers who can be regarded as the family which ruled banking.
The round-trip presented as the formula for IRP.
You will be able to write IRP as a particular formula. You can refer the $/=C rate of exchange x0. You need to take the forward rate of exchange that you can fix in August 2003 for exchange to take place in August 2004 x1. The arbitrage relationship follows:
If you wish make this formula simpler, and write in a standard manner signifying the IRP equation then you will get Formula 25.1.
IMPORTANT:
The covered IRP is a condition of arbitrage which signifies that the exchange rates on forward transactions as well as currency spot have relation with the interest rates of specific countries by the formula
The rate of exchange of currency can be termed as x and is defined as $/=C. the x1 can be regarded as the rate of forward exchange during time 0 so that an exchange takes place on course of the future time of 1. In the example that has been taken here, 1.0783 $/=C/1.0886
$/=C ≈ 1.0112/1.0209. This particular formula is quite easy to memorize. The rates of interests of the dollar and the euro are similar in nature as the rate of exchange. The dollar is put at top and the euro below it. In order to make things clearer for readers, the right hand side is a repeat of the left hand side. The name of the forward rate is presented as f and the spot rate indicated by s.
The IRP of uncovered nature is merely a hypothesis of economics and not necessarily condition for arbitrage.
You need to understand that the rate of forward exchange is not necessarily the rate of exchange for the future spot. Thinking on this line is quite similar to addressing the forward rates of interest as spot exchange rate of future. You will remember that it was taught in section 5.4 that there exist two explanations for the high value of the forward rate of interest. The interest rate of the future can easily be greater than the interest rate of the present times. Different investors may ask for compensations of risks and wish to have term bonds of longer duration. The forward rate of exchange can differ from spot rate of exchange for two similar reasons stated here:
The rate of spot exchange of future times can definitely be deemed as different from the spot rate of present times.
All the futures contracts which are one sided in nature have to be provided with compensations for their ability to carry on the risks.
You require believing that there are no compensations for risks and the fact that future exchange rates would be the top most expectation when it comes to rate of spot exchange in the coming future. This can also be referred to as IRP of uncovered type. For this particular case, you will be able to exchange the forward rate in the covered IRP with the spot rate of the future which is expected to come. The forward rate which is prevalent presently, can be regarded as a completely neutral predictor of the spot rate of future s1: f1= E (s1). However there are few reasons to believe that this is the usual scenario.
Solve now!
25.1 C Purchasing Power Parity
Why are rates of interests varying across different countries?
The question presented here is simply not concerned with money, but also about all those goods.Should these goods cost the same amount of money in various places? If these goods cost accordingly, then you have a PPP before you.
The forward rate of exchange is precisely got by the interest rates from an arbitrage. There is quite a serious question presented here, this is regarding whether the rate of interest in terms of euros is greater than that of the U.S. dollars. The different economists are not quite sure which one is better. Another important fact is regarding whether the PPP holds true. The PP P theory concerned with rate of interest states that process of the same goods need to be same in all countries. The costs can only vary when transport costs and other such duties are taken into consideration. The PPP needs to hold. You may have the question whether you can purchase the same number of apples with 108 dollars as you can with 100 euros. If one apple costs 1.08 dollars in the US and 1 euro in Europe then the PPP can be said to hold true. Also you will be able to bring in the apples at a cheaper rate from US and sell them at a profit in Europe. The costs involved with transport as well as tariff barriers present prevent this type of apple based arbitrages. There are however many different goods which can be transported easily, these goods include, gold, gas as well as diamonds. The economists have to say that the prices of those goods which can be transported easily need obeying the PPP.
All the different goods cannot obey the PPP. For example the landscape of France is not same as that of the USA and hence it cannot be imported or exported. The material concrete is too much pricey to be transported from one place to next because of the too high costs of shipping the materials. The raspberry fruit also gets spoilt very easily when it has to traverse long distances. The maple juice does not have too many takers in the Europe. The kind of styling that a Czech would do to your hair is not same as the treatment you get in an American salon. The list is endless. PPP is such that it may not be consistent inside one particular country. The cost of houses as well as hiring of plumbers is more in San Francisco than in the town of San Antonio. Intra country PPP is a failure just as it does not hold true across countries. When the costs of transportation is taken into account, and still the cost of gas in San Francisco is greater than that in San Antonio, then in order to make profit, gas will be shipped from Antonio to Francisco quite soon.
If for a minute it is assumed that PPP holds well every time, then different commodities having different rates of interest would be defined by various rates of inflation. If an apple costs 1.08 dollars in US and inflation rate is 2% then after a year, it will cost 1.11. A forward based rate of exchange rate can be locked on. In European countries, one apple costs 1 euro presently and would cost 1.0298 the coming year. Hence the rate of inflation in Europe would be nearly 3%. One of the effects of PPP is that the actual rate of interest has to be same across the different countries, actually equal. The interest rate being deemed as real is actually a nominal kind of interest rate which has undergone adjustment owing to inflation. Your money can be compared to the good quality apples. Owing to inflation these apple’s price may drop down a little bit but will gain through the earnings it makes through interests. Hence the PPP claim is here
Here the r term is interest of nominal type and π is rate of inflation. The PPP in itself is quite strong in nature. The PPP always hold greatly for those goods which get transported regularly using the quickest method. These things will definitely be with you during a long course of the day. The setting up as well as importing and exporting of goods is a time consuming process. There are various forms of the PPP formula. Some investors can earn a bonus since they have gone through the extra hurdle of transferring the money.
Don’t forget: PPP is a completely interesting assumption based on the fact that is not quite going to work around you always,
ANECDOTE
Yale’s Most Famous Economist
Irving Fisher is arguably one of the best economists ever. But the personal life of this person is quite colorful too. He is the person who invented the concept of what is known as today as Fisher hypothesis. It was in the year 1892 that Fisher wrote his dissertation. He actually constructed a machine full of levers, pumps as well as wheels in order to provide a demonstration of his theory. You will find these images on Google. He was a big supporter of maintaining healthy eating habits. The index card system that he had made helped him make a lot of money. This is also called rolodex system and is a banking system. The infamous Wall Street Crash that took place in the year 1929 damaged his reputation as well as financial condition severely. This is because even few days before the crash, he would assure the different investors that the prices of the stocks had not got inflated but rather achieved a plateau. This shows how even geniuses can be proved wrong by the uncertainty of the financial market.
IMPORTANT:
If the theory of PPP holds true, then all the different goods would be priced the same in various countries. The differentials concerned with the rate of interest can hence be represented by the differentials for inflation rate.
Going by the hypothesis of Fisher, the rates of return which are expected have to remain same irrespective of the country or state.
In real life, you will find that various commodities follow the PPP in different ways. There exists no duty on the import of the gold between European countries and the USA. Hence here the PPP holds quite well. For other goods, the PPP may or may not hold good. It all depends upon how good the market for a particular commodity is. There are few goods which are quite similar to each other. The inflation rate being reported here is according to an arbitrary bunch of commodities, denoted by the CPI. You may ask for evidence regarding these facts or hypothesis. In practice the countries having greater rates of inflation on an average should have a currency exchange value that depreciates constantly. This has to happen under the rule of PPP. The answer to this is yes, but in a really weak manner, it usually takes place by gaps of 1-5 years. When longer period of time is considered, for example a decade or two, then you will find that there exist firms which work extremely hard to ensure that the theory of PPP comes true in real life or at least there are some close deviations from it. Hence it can be concluded that PPP will better over longer period of time rather than short time interval. Different kinds of forces existing in the market take the side of PPP.
PPP will hold good for those goods which can be transported easily. However for goods which are difficult to transport, the same cannot be said. You will also find the PPP being better over a long duration of time.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction of corporate finance
- The time value of money and net present value
- Stock and bond valuation annuities and perpetuities
- A first encounter with capital budgeting rules
- Working with time varying rates of return
- Uncertainty default and risk
- Risk and return risk aversion in a perfect market
- Investor choice risk and reward
- The capital asset pricing model
- Market imperfections
- Perfect and efficient markets and classical and behavioral finance
- Capital budgeting applications and pitfalls
- From financial statements to economic cash flows
- Valuation comparables financial ratios
- Corporate claims
- Capital structure and capital budgeting in a perfect market
- The weighted cost of capital and adjusted present value in an imperfect market with taxes
- What matters
- Equity payouts
- For value financial structure and corporate strategy analysis
- Capital structure dynamics firm scale
- Capital structure patterns in the united states
- Investment banking and mergers and acquisitions
- International finance
Links of Next Financial Accounting Topics:-
- Investments in foreign financial markets
- Capital budgeting with foreign cash flows
- Corporate currency hedging
- Who are you working for
- International finance
- Options and risk management