Conservation of linear momentum states that an object retains total momentum and considered as isolated until and unless any external force acts on it. In other words, without the application of an external force, the body or an object will converse the momentum. It can be formulated as,
Since resultant force is zero,
2 – 1 = 0
Or,
2 =1 (This is the principle of conservation of linear momentum.)
Note:
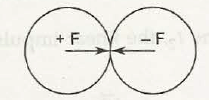
Suppose two bodies collide with each other as shown in figure below.
If one body has +F and other body has –F, then the net force will be zero {(+F) + (–F) = 0}. Here, the linear momentum is conserved.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Position vector velocity and acceleration
- Plane kinematics of rigid bodies introduction
- Combined motion of translation and rotation
- Rectilinear motion in kinetics of particles
- Work and energy
- Linear momentum
- Linear impulse
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-