An internal combustion engine where it is the piston that complete all the 4 separate stokes while a crankshaft is turned is known as Four stroke engine or Four cycle. A stroke is referred to as complete traveling of piston along cylinder area in various directions.
There are 4 strokes in this regard:
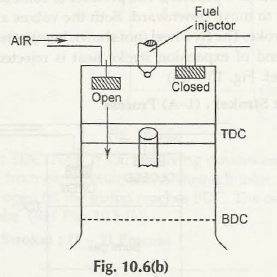
- Induction/Intake:
The piston stroke begins at the top center and ends at the bottom center. Valve has to be in the open position and cylinder through its downward motion.
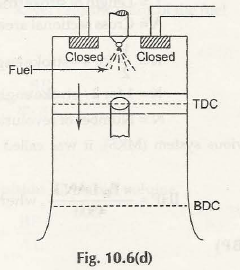
- Combustion:
It is the ignition and starts off when crankshaft has completed the 360 degree revolution
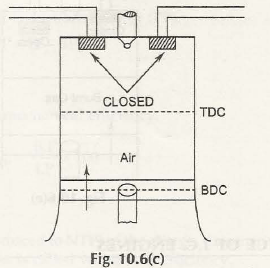
- Compression:
The air-fuel mixture is compressed in this format and both intake and exhaust valves are closed.
- Exhaust:
It is the outlet that is used for expelling air-fuel mixture.
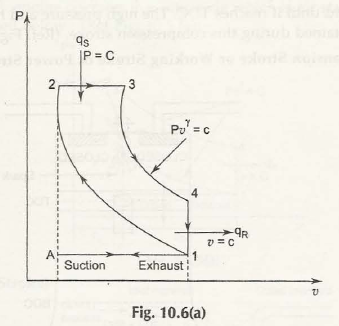
Stage 1 Suction Stroke (Process A-1)
Stage 2 (Compression Stroke) (Process 1-2)
Stage 3 Expansion Stroke (Process 3- 4)
Stage 4 Exhaust Stroke (Process 1-A)
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Open system and control volume
- Conversion of work into heat
- Introduction to carnot cycle
- Clausius inequality entropy and irreversibility introduction
- Ideal gas or perfect gas
- Introduction about air standard cycles
- Diesel cycle
- Operating principle of four stroke petrol engine s i engine
- Operating principle of four stroke diesel engine c i engine
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-