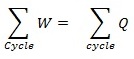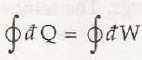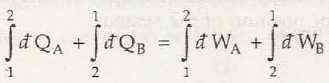The first law of thermodynamics deals with laws of conservation of energy and this energy cannot be formed or destroyed, but it can certainly be transferred from a single form of energy to another form of energy.
It is said that energy can be conserved. Heat and work and known as two different types of energy. In case heat energy is supplied to system through surrounding then system would come up with work energy to surrounding and similarly if the work is done upon system, then system delivers energy in form of heat to surrounding.
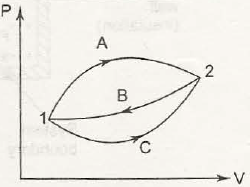
It is said to be the basic concept related to first law of thermodynamics. When it comes to first law of thermodynamics for closed system undergoing a cycle it is important to understand the algebraic summation of energy transfer which signifies heat energy transfer as well as work energy transfer which would be through system boundaries and it will turn zero.
You can take a note in case the system that does not undergo any cyclic process and one of the systems is undergoing the change of state, and then the above equation may not be applicable.
So, the net amount of energy can be stored within system during the process is (Q-W) which will signify the net energy and this will accumulate within system and there will also be increment in any internal energy of system as (Q-W) which says that the amount of energy that gets stored within system during a cyclic process.
When it comes to first law of thermodynamics, it is important to maintain the equation of thermodynamic process in case the system is under any change of state.
Q-W = ∆E
Where,
∆E is related to increase in internal energy of system
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Statically indeterminate system
- Introduction to thermodynamics
- Statement of zeroth law of thermodynamics with explanation
- Heat and work introduction
- First law of thermodynamics for a control mass closed system undergoing a cycle
- First law of thermodynamics for a change of state for a control mass closed system
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-
- Different types of stored energy
- The constant volume specific heat
- Enthalpy
- The constant pressure specific heat
- Specific heats of solids and liquids
- Energy of isolated system
- Perpetual motion machine of the first kind pmm 1
- Open system and control volume
- Conversion of work into heat
- Introduction to carnot cycle
- Clausius inequality entropy and irreversibility introduction