Resource Allocation
Once achieving the goals of an organization it gets vital to find out how they had been achieved. The organization must have resources before leading towards their goal. These are the organizations assets for fulfilling the goals effectively. Resources can be chosen with number of techniques this will be discussed better through budgeting, breakeven point, linear programming and scheduling.
 What is budgeting?
What is budgeting?
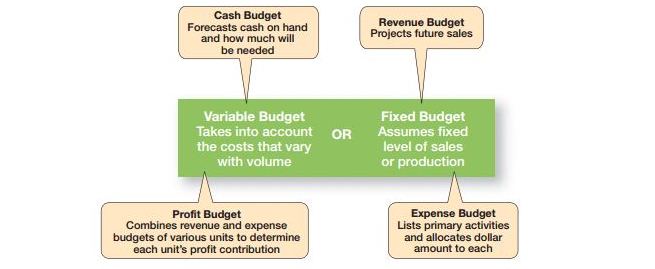
Often it has been seen that we had an experience with limited budgets. We had also learnt that unless we are done with allocation of our resources the weekly allowance was over. Thus a budget is a form of numerical value that allocates the resources to varied activity. Managers prepare revenues, capital expenditure and the expenses. It is not unusual for all the budgets but yet improving the time and space along with resources would help for better budget set. These categories of budget are for discriminating the non-dollar budget with those of a dollar budget. Items would include as person-hours, utilization of capacity, production units proper usage are all meant for budget that too for daily or weekly basis or even for monthly basis too. Exhibit PM-3 would describe more about the three different types of budget services.
 Scheduling:
Scheduling:
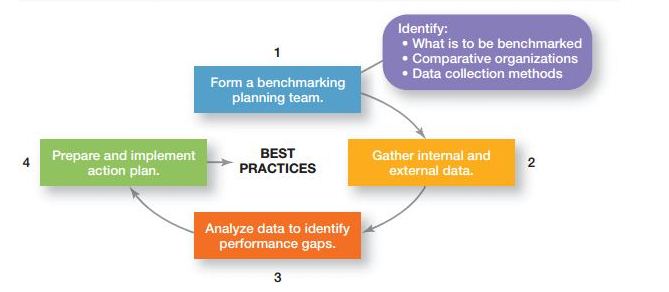
Jackie the manager of Chico’s stores from San Francisco does a task of calculating the work time of each employee with their work space an also the location of each employees in a week. If you have ever observed a group of managers doing similar work then allocation of resources for the activities that can be done, in what ways they can be done, and when will they get completed. These fall under the scheduling process. Here few of the scheduling devices will be reviewed using the Gantt charts, PERT network analysis and load chart.
GANTT CHART:
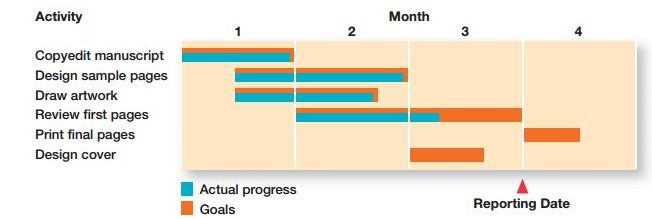
This type of chart is developed in the 1900’s that too by Henry Gantt who was the associate of scientific management experts team under the rule of Frederick Taylor. The idea used for these charts are quite simpler. Basically this chart is essentially using bar graphs created upon horizontal axis whereas the activities are listed upon vertical axis. These outputs being planned as well as the actual one both are seen with these graphs over that period of time. With the help of these Gantt chart you can also find more about what kind of tasks needs to be completed and also compares them with original task. It has helped managers with a detailed about the project completion and also to check whether that project is done before or on time.
The Exhibit PM-5 is completely depicting the Gantt chart especially for production of books being published by the company. The time is shown on top of chart. Work is shown down left side of the chart. Planning is definitely the deciding factor for which kind of work or activity can be completed. It also includes the order for which the activities are done with allocated timings. If a box sits easily within this time frame then this becomes its planning sequences. The portion of the shading is the reflection of actual progressing taking place. This chart is a form of controlling tool that shows the deviation of planning. Here in the example, the designing of cover along with reviews from the first page is genuinely running less than the scheduled time. The design on the cover are made three weeks ago that but still there has not been any kind of progress. These linings are shown by the blue colors. In fact the review being mentioned on first page is from two past weeks being scheduled. With this information about the manager should be able to take few actions for either making last two weeks work done or else estimating that there is no such delay further. If no actions occur then the book could be expected to be published two weeks back by the managers.
 LOAD CHARTS:
LOAD CHARTS:
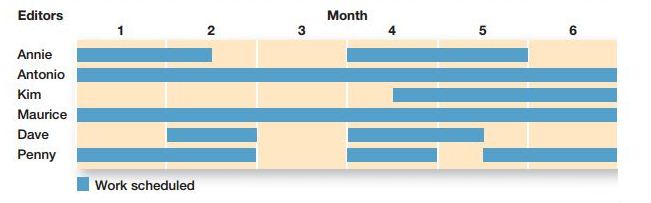
When a Gantt chart is modified then the new version is called Load Chart. Listing is done on the chart as per the resources. This helps the manager to easily make planning and also control utilization capacity. This chart schedule as per the capacity of working areas.
For instance, the Exhibit PM-6 has shown the entire load chart with six productive editorials from same company. Each of the books is supervised by the editor. By doing this supervision the editor could decide who is ready for accepting the new books. If in case all the projects are been full then the editor would automatically not accept any of the new projects for avoiding delays. As per the Exhibit, Antonio and Maurice are completely ready for projects till 6 months. Even it may happen that some editors might be present for helping other with their available unassigned time period.
 PERT NETWORK ANALYSIS:
PERT NETWORK ANALYSIS:
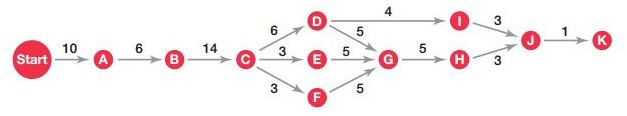
Until the activities are less in number the Gantt chart and Load charts could be useful. But as the number increases then the concept of another analysis process comes to existence. What would happen when your manager has to plan for some large project? This may include reorganization of departments, cost reduced programs implementation, new projects development for marketing, and products designing’s? These all require thousands of coordination from varied activities. From these few are done in a simultaneous manner whereas few are done when predicted. Similarly preparing building walls are the ultimate foundation of construction. Then how could a manger go for complex project selection? This Program Evaluating and Reviewing Technique have been of great importance.
This PERT network is designed for depicting varied sequence of activity required for any projects completion. With the help of these PERT networks it gets easier for managers to determine which type of events needs to be done and in what manner. In fact comparison also gets easier with this PERT. Managing the progress of project can also be done by managers using PERT network analysis.
To learn the construction of PERT network what you need is to know about four major terms. These are Events, Activities, Slack Time and Critical path. Events are represents the project’s completion. Activities are the time required for resource progress. Slack time means the time delayed by individual work. Critical path the most time capturing path in the PERT analysis. Any delay would make the entire end project is delayed. Activities being done over this path have lower slack value.
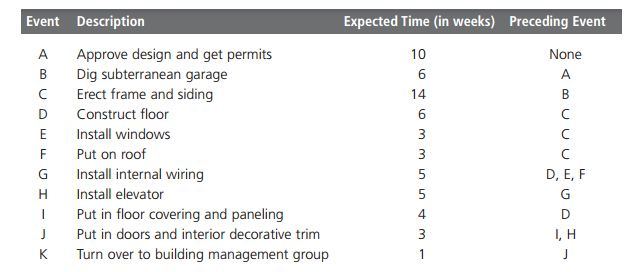
Before the development of PERT network the manager should identify all activities need. Then these should be ranked systematically with estimated completion timing. Exhibit PM-7 is representing this process well.

A-B-C-D-I-J-K (44 weeks)
A-B-C-D-G-H-J-K (50 weeks)
A-B-C-E-G-H-J-K (47weeks)
A-B-C-F-G-H-J-K (47 weeks)
This PERT network being created by you shows the project would be completed well within 50 weeks’ time if all goes well. This calculation is made by tracing paths through longest path: A-B-C-D-G-H-J-K and then add up all the time. You know well that any kind of delay would delay the project. Completing the same floor with covering and paneling would not affect any of the projects date. This is so as the operation is not done on the right path. But taking the time period of 7 weeks rather than 6 for digging of subterranean garages is likely a delay through project. For completing within less time definitely the manager would focus more upon critical path. If any other activity is not being done on those critical path then that would be chosen for critical path.
 Breakeven Analysis:
Breakeven Analysis:
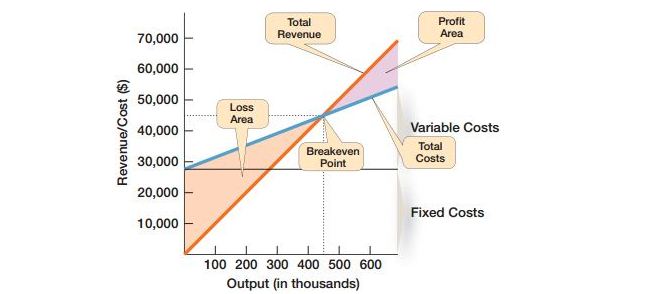
Managers at the Glory foods corner wanted to learn how many of the seasonal vegetables could be sold such that this could easily break even. Thus it means that a point for which revenue is enough for covering all costing. Breakeven analysis has been widely sued by the team of resources allocation techniques with the help of managers such that a breakeven point is determined.
This breakeven analyzing is the simplest one for calculation. Thus it is still valuable for managers as they point towards the relationship of revenue, profits and costs. In order to make a computation of breakeven point (BE) manager is required to learn about price of products being sold that too in units (P), variable cost (VC), and total fixed costs (TFC). Breakeven occurs when the total revenue of the organization is sufficiently enough for equating the total costs. Total costs had two parts like fixed cost and variable cost. These fixed costs remain unchanged regardless of their volumes. For example, insurance premiums, rents and taxed of property. But on a contrary the Variable costs keeps on changing in proportional of outputs. These include raw material, cost of labor and energy costing.
This breakeven can easily be understood with a graph using formula:

- Total revenues are equal to the total cost when products are sold at variable cost.
- Differences in between the price and that of variable cost would give a number for units being sold.
Here is an example for better understanding. For example take Randy’s photocopying service usually charges $0.10 per photocopies. Fixed costs are $27000 a year whereas the variable cost would be $0.04 per copy. While computing this breakeven point becomes: $27000/ ($0.10-$0.04) =450000 copies or even the annual revenues would be $45000 / (450000 copies x $0.10). This is same relationship for Exhibit PM-10.
As for a panning this could easily help randy while building up the goals. For instance, Randy could even make determine the profits and slowly will calculate sales level for reaching goals. This Breakeven point would also show how much the volume of sales needs to be increased.
 Linear programs concept:
Linear programs concept:
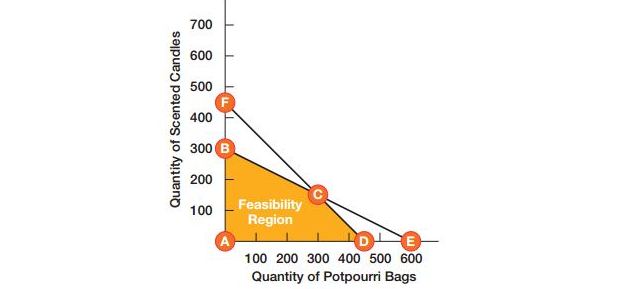
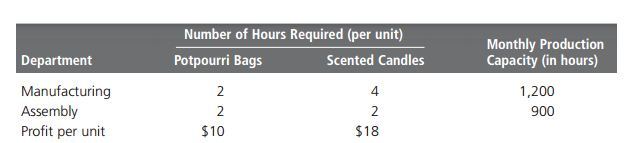
Maria Sanchez has been manufacturing plants which can produce cinnamon scent product one is the wax made candles and other would be woodchip potpourri bags. This business is profitable as she could also sell all her goods easily. But her dilemma was that: though both these are been manufactured in same sense but what number of them produces profits? This is called as Linear Programming for solving resources allocations.
Linear programming can easily be also applied to all resources allocation problems for getting outcomes of varied goals. This is combining with different methods for varied outputs. In case of Maria’s business the ultimate condition is met only when they took double the amount of all raw material and long hours by labors for production of products meant for home with great fragrance.
Now what type of issues are resolved using linear methods? Selecting proper routes for transportation would automatically reduce shipping costs, allocate a budget that is limited for advertisements, optimal assignments done for projects, and determine what kind of project can be made with certain resources. Now let’s see how Maria has been using linear programming or her issues. This is the condition of the complex and linear problems and here programs that can be used for minimal solutions.
What we all need to do is find facts of that too of Maria’s businesses. Profit margin would be $10 for a simple bag and other $18 for candle. Then the maximum profit would be = $10P + $18S, where the P represents number for bags and S represents candle number. This is a simple equation of mathematics. But Maria is aware of the time period she would require spending behind production and her monthly producing capacity for both manufacturing and assembling. For better understanding have a look at Exhibit PM-11. Production capacity would include numbers like constraints on the capacity. Now the constraints would be:
2P + 4S <= 1200
2P + 2S <= 900
Maria also state P>=0 and S>=0 because the products of fragrance can be easily produced within less volume.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- management and organizations a managers dilemma
- Understanding managements context constraints and challenges
- Managing in a global environment
- Managing diversity
- What is social responsibility
- Managing change and innovation
- Managers as decision makers
- Foundations of planning
- Strategic management
Links of Next Fundamentals of Management Topics:-