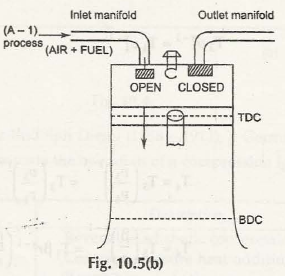
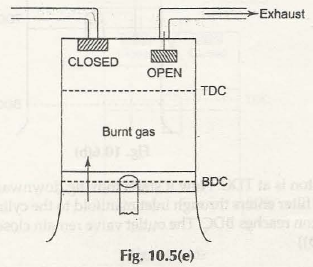
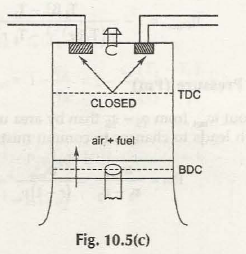
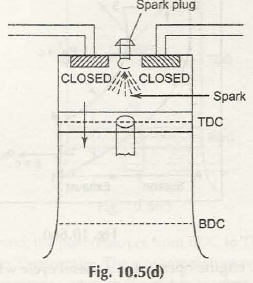
When Otto Cycles are considered, the working is based on Four Stroke Engine as well. The power level that is produced by this Otto Cycle is energy that is developed at per unit of time. Hence, specifically in this case, both intake and compression of stroke take a single rotation of the crankshaft.
When the power and exhaust stroke is considered, it is another rotation that is taken into consideration. So, it can be well said that if you are planning on getting the perfect operating principle of this whole system, both these rotations have to be taken into consideration and each of them have to be differentiated from each other.
Operating Principle of Four Stroke Petrol Engine (S.I. Engine)
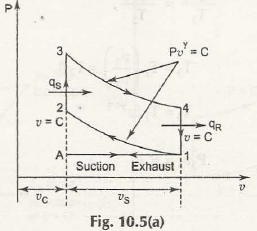
Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic compression
Process 2-3: Constant Volume Heat Addition:
Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic expansion
Process 4-1: Constant Volume Heat Rejection
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Open system and control volume
- Conversion of work into heat
- Introduction to carnot cycle
- Clausius inequality entropy and irreversibility introduction
- Ideal gas or perfect gas
- Introduction about air standard cycles
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-
- Operating principle of four stroke petrol engine s i engine
- Operating principle of four stroke diesel engine c i engine
- Performance of i c engines
- Properties of pure substances introduction
- Vapour compression refrigeration cycle introduction
- Basic fluid mechanics and properties of fluids introduction
- Fluid statics introduction
- Manometers measurement pressure