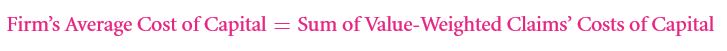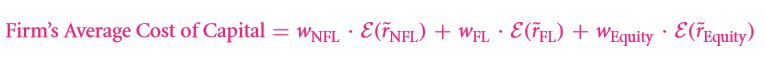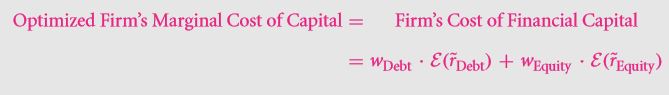The liabilities as far as the figure 15.1 is concerned, is thrice its debt. This is something that is extremely common as far as the various US based companies are concerned such as IBM. A question that definitely ought to come up here is whether or not the propositions made by M & M still hold.
16.6 A VALUE IRRELEVANCE
To begin with, let us first go back to the proposition made by M & M. The way these visualized the perfect world. The capital cost is without a doubt independent of the manner in which the various projects are financed. Under most circumstances, the task of trading a capital structure that is dumb at an extremely low price becomes exceedingly difficult. In comparison to this, a capital structure that is optimal can be easily sold at extremely high rates. The two major aspect of the perfect market as proposed by M & M that ought to come in handy in this section are as follows:
- The utmost elasticity exists as far as the market with capital is concerned. Most of the claims that a particular firm would dream off are to be taken away.
- As far as the claims of the firms and the various operations carried out by the firms are concerned, there are not linked in any manner.
The assumptions stated above do not hold as far as the liabilities that are not financial are concerned. Listed below are a few instances:
- Liabilities on Income Tax: 15th April is considered to be the tax day. If an individual fails to pay his or her taxes by this day, he or she can very well use the liabilities of his or her own purposes. However, if the rate of interest is zero, then it is for certain that an individual won’t be able to make much out of it.
- Credit for trade: As far as the suppliers are concerned, they often provide their clients with supplies at a credit on which no interest rate is charged. These sort of transactions are entirely based on turn. There are certain goods that individuals won’t even purchase in the event that appropriate credit hasn’t been provided for the trade. Such a capital structure having trade credit is by all means better than structures that don’t have one.
As per the equation 16.1:
If you follow the propositions that were laid down by M & M, the NPV = 0. However, the credit for trade at an interest rate of 0 % will without a doubt have a positive impact on your NPV. This may in turn encourage the business owner to opt for various other operations. This depends on whether a supplier provides credit for trade or not. This is an extremely vital aspect in the event that a particular individual wants his or her business to thrive. In order to satisfy the various propositions laid down by M & M, individuals might as well propose scenario within the perfect world without he claims that are nonfinancial. This however, isn’t that much important due to the fact that this chapter is mostly concerned about the claims having a financial background. In addition to this the markets that aren’t financial are nowhere close to being perfect. With so many differences between the perfect world and the real world, it is for certain that these propositions won’t be of much of a use. But the fact remains that individuals must without fail look at the claims from a bigger point of view. Another thing that must be taken into account is the fact that the M & M propositions don’t hold for firms with liabilities that are not financial. In the event that the various operation that a firm needs to carry out hasn’t been fixed,
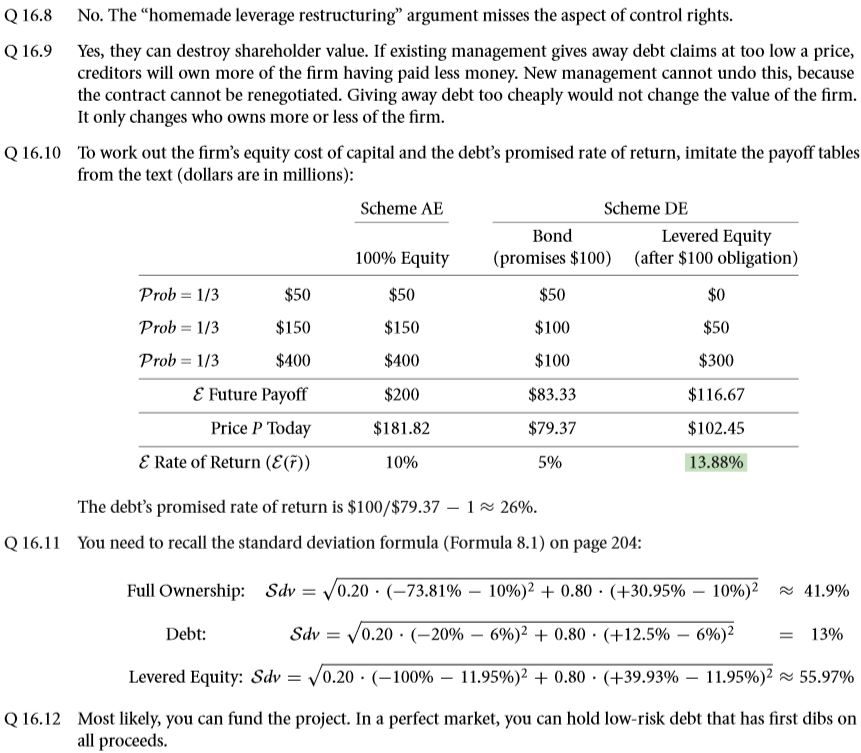
- According to M & M’s ordinary propositions, the arrangement of the claims be it financial or non-financial, doesn’t guarantee its indifference towards the firm value.
- In the real world, the M & M articles say that it is only the financial claims of a particular firm don’t vary with distribution of equity and debt.
SOLVE NOW
16.6 B THE MARGINAL AND WEIGHTED AVERAGE COSTS OF CAPITAL
All along, we have visualized the world of M & M to be somewhat similar to the perfect world. However, let us now move into the various aspect of the world that was proposed by M & M. The capital cost that is marginal is only applicable to the next $1 that ought to be earned. The Capital cost that is average is considered to be a milestone of the various projects of the firm. This however, is not that relevant but it is in turn considered due to several smaller aspects. However in the world proposed by M & M, both of these costs are considered to be same which further reduces the complexity of the various operation. However, in case of the real world, the two are not the same under most circumstances. Hence, make sure that you have a firm idea regarding both before you actually step into the real world environment.
At first the existing investor of the firm needs to be considered. Once this is done, the WACC must be calculated. Even for a project that is limited to a particular firm, the capital cost to be considered is the average not the marginal cost.
Recall the following equation:
This can further be reduced to:
The idea of the equity or the debt being +ve or –ve projects of NPV is annihilated. Thus in the event that individuals are looking forward to swapping between the weighted equity and debt, they can do so easily as it won’t have any sort of impact as far as the firm value is concerned. If you consider NFLs, you may write the equation as:
Here FL and NFL stand for financial and nonfinancial liabilities respectively. However, the problem with this equation lies in the fact that the NFLS cannot be adjusted as and when required. The risk adjustment factor of capital cost varies greatly as far as the various projects are concerned. As already mentioned, individuals must try and ensure that they clear the taxes by 15th April which is considered to be the tax day all across the globe. There are various financial strategies that a particular firm may opt for. In this case, the best option would be to opt for the source where the marginal cost involved in minimum.
- Consider a scenario where in the finance source that is cheapest is linked with a particular project. The manager here must without a doubt make this a part of the benefits and expenses of the project. This will definitely have a huge role to play in the long run. In the event that suppliers aren’t willing to provide trade credit, then you might as well not carry out any sort of future transactions with that supplier.
- In the event that the finance source is linked with the firm itself, the project selection process certainly won’t depend on the source. If you are aware of the existence of equity debt and marginal costs in the perfect world, then it is for certain that you will be able to make some huge profit. Once you reach the panicle of success in the field of finance, one thing is for certain that you will look at financial claims as an effective ally.
In both the examples, individuals have opted for the NFLs that are cheapest. As a result the manager is greatly dependent of the capital of the perfect world. This in turn is considered to be the marginal cost for your company.
IMPORTANT:
- All the capital finance sources would have been used up by the various companies in the event that the finance sources weren’t linked with individual projects.
- If a company has exhausted its NFLs in the perfect world, then the marginal capital cost is the cost of equity and debt.
- If the nonfinancial sources of finance are linked to individual projects, the sources themselves end up as a component.
- The proposition of M & M still hold as far as the claims of finance are concerned.
- As far as the average and the marginal capital costs are concerned, both are the same.
While going through these chapter, one thing must be kept in mind, i.e. M & M usually focuses on the structure of the capital only. There are in no way applicable as far as the real world is concerned. For the propositions to hold, the perfect world needs to be considered. There are the topic that ought to be discussed under the chapters that are to follow.
SOLVE NOW:
SUMMARY
Some of the major topics to have been covered under the scope of this chapter is as follows:
- Maximization of the value of the firm should be the sole object of a manager. He or she must be concerned as far as the value of the shareholders are concerned. If these don’t follow these guidelines, they definitely stand to be replaced.
- According to the propositions laid down by M & M, as far as the perfect market is concerned, the value of a firm is unaffected by the manner in which the firms are financed be it with equity or debt or both.
- The owners often provide various incentives so as to attract investors and to ensure that the capital structure is maximized.
- In case of poor choice of capital, arbitrageurs are used to eliminate them.
- If the arbitrageurs are competitive enough, they can very well purchase the flow of cash as well as have command over various rights.
- Financing through debt doesn’t increase the capital cost.
- The capital cost of a firm is divided among equity and debt.
- The CAPM works only for the perfect world as assumed by M & M.
- Suppose the capital cost that is expected on the equity is x, a bank may ask for a rate that is greater than x.
- In case of the market that is perfect, the average and marginal capital costs overlap.
- NFLs aren’t very common to the perfect world.
- If a firm depletes its NFLs that were available at low costs, then the funding in the elastic world becomes the capital source that is marginal.
- The financing is considered to be a part of the project in the event that it is extremely cheap.
KEY TERMS
576 – > Modigliani-Miller
601 – > average cost of capital
574 – > ex – post , ex – ante
586 – >cost of capital
573 – > fiduciary duty
587 – >weighted average capital cost
601 – >marginal cost of capital
587 – > WACC
573 – > board of supervisors, shareholder wealth maximization
575 – > Capital structure that is optimum
576 – > M&M
SOLVE NOW! SOLUTIONS
PROBLEMS
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction of corporate finance
- The time value of money and net present value
- Stock and bond valuation annuities and perpetuities
- A first encounter with capital budgeting rules
- Working with time varying rates of return
- Uncertainty default and risk
- Risk and return risk aversion in a perfect market
- Investor choice risk and reward
- The capital asset pricing model
- Market imperfections
- Perfect and efficient markets and classical and behavioral finance
- Capital budgeting applications and pitfalls
- From financial statements to economic cash flows
- Valuation comparables financial ratios
- Corporate claims
- Capital structure and capital budgeting in a perfect market
Links of Next Financial Accounting Topics:-
- The weighted cost of capital and adjusted present value in an imperfect market with taxes
- What matters
- Equity payouts
- For value financial structure and corporate strategy analysis
- Capital structure dynamics firm scale
- Capital structure patterns in the united states
- Investment banking and mergers and acquisitions
- Corporate governance
- International finance
- Options and risk management