Investment banks provide advice to firms on mergers and acquisitions. Merger is defined as the partnership between two corporations on an equal basis. An acquisition is defined as a situation when a corporation buys the other. Tender offer is followed where the shareholders present their share in exchange of stock or cash. Investment banks facilitates this process and handles the legal aspects of the situation.
ANECDOTE: RJR, EGO, AND OVER PAYMENT
Let us talk about the takeover battle for RJR Nabisco between Kohlberg Kravis Roberts and RJR management. In the month of October 1998, RJR’s CEO Ross Johnson and his predecessors had taken several wrong decisions and offered RJR shareholders a price of $17.6 billion in a leveraged management buyout. The CEO had to resign because of his conflicting interests with the shareholders. A counter offer of $20.6 billion was offered by Kohlberg Kravis Roberts. Though KKR was able to purchase RJR for $25 billion, but, overall it was a loss as RJR was bought at an overpriced amount. The main reasons behind this wrong decision was ego and person enmity which led to an irrational bidding war. But it led to RJR shareholders earning benefits.
The sources of values of a leveraged buyout are as follows:
- Control on the agency conflicts.
- Using debt to reduce corporate tax obligations.
If we are talking about a typical leverage buyout, the acquitter restructures the existing management-compensation contracts so that managerial incentives can be improved. When management occurs, the existing management becomes the LBO buyer.
In case of a hostile takeover, the corporate raider will make an offer to purchase the shares so that the firm be acquired or a voting majority can be won. If the acquitter is successful, he can appoint new board members to run the management.
23.3. A Reasons for Mergers and Acquisitions
Managers often want to acquire more companies because running a huge and successful company more prestige and power. But it often happens that due to the poor performance, the managers get dismissed and ultimately the acquisition profits only the shareholders. There are several factors on which acquisition depends. Let us read about these factors.
Value Change
Following are the causes of corporate value gains:
- Scale synergies: It leads to increase in efficiency due to merger of skills, structures, departments and staff. Gain in efficiency can result from the following sources:
- Duplicate departments can be eliminated and fixed overheads can lower the operating costs.
- Production and distribution efficiencies can attract more bank customers.
- Market imperfections can be reduced.
- Reduction of competition: Elimination of targets from competition results in increase of prices.
- Expertise: Purchasing a firm is easier than building expertise for the acquirer.
- Elimination of poor target management: If current management system is not able to perform, it should be replaced by an efficient team in order to provide value gain.
- Shutdown efficiencies: When the best option is to liquidate or shrink a firm but the management is not allowing so, a takeover by an individual with lesser known institutional history makes the situation better.
- Expropriation: It is not possible to contract out all the promises which the employer makes to the employee. Some things are based on trust.
Other important value gains which are assumed in acquisitions, leveraged and managed buyouts:
- Tax benefits: High debt ratio results in reduction in the amount of taxes.
- Better governance: The need to service debt makes it convenient for the manager and employee to work hard and spend less on pet projects.
Sometimes, takeovers fail in delivering value enhancements. The negativities of a takeover are drifting of focus, more bureaucracy and poor management system. A company suffering from poor management will notice that their manager will purchase other companies for the management sake and not for the sake of the shareholders. The acquiring managers can benefit from the following:
- Idiosyncratic risk reduction: The scale of the firm is increased by takeovers. This in turn reduces the idiosyncratic risk and increases the firm’s earnings and revenue.
- Large empire: More compensation is received when managers run a big firm.
But in 1980s, a reverse situation was observed. Larger conglomerates were taken over by smaller firms. The negatives observed in those cases were loss of benefits of easy access and less diversification.
Solve Now
- If the firm has decided to fire workers that cost more than they are producing, is this a sign of better governance which is following the interest of society?
- List the main sources of value generated in most mergers & acquisitions.
Value Change Beneficiaries
In order to know who among acquiring shareholders or targeting shareholders benefit the most from net value changes, you need to consider the scenario in terms of an efficient market where the targets are priced in such a way as if the acquirer has not yet made his presence. Following are the assumptions:
- If the target is purchased at original market price, then the gains and losses that the acquisition will produce will go to the acquirer.
- If the target is purchased at a price higher than the prevailing ones, some of the merger benefits will go to target shareholders.
- If the target is purchased at a price which include the cost of all benefits, target shareholders will benefit and the acquiring shareholders will be end indifferently.
- If the price on which the target is purchased is even higher, the acquiring shareholders will end up having a loss.
Summary
In general, when an acquisition succeeds, acquiring managers gain profit and target managers suffer a loss. But the case is opposite for shareholders. Other than managers and shareholders, other parties are also involved in a takeover. They are investment banks, other stakeholders such as employees, suppliers and customers. After the acquisition has taken place, if it is well managed, it will have benefits in the long run.
Solve Now
- If the value of the acquisition is increasing, can it have any bad effect on the acquirer?
- Why is it that firms like to acquire other firms?
23.3 B Resistance to Corporate Control Activity
Target management can resist a hostile takeover by following certain steps which are collectively known as shark repellents which are described below:
Greenmail: The money of the shareholders is used by management to buy off the acquirer share. This bring bad publicity and hence is rare.
Golden parachute: Management is bought off with a large bonus by the acquirer.
Acquisitions: The target management buys other companies, because acquiring a bigger company is difficult. This strategy is also known as blowfish defense.
Scorched earth: Management threatens to sell off corporate assets which interest the acquirer.
Poison pill: When a poison pill is triggered, it entitles other shareholders to purchase shares at a discounted price. The raider would now have to repurchase these shares at the acquisition price.
New share issuance: Management issues more shares to their employees and to themselves. High severance packages are promised to for any employee who wants to leave if the firm is taken over. The acquirer would then have to repurchase more shares and pay more to the employees.
Fair value provision: A fair value provision forces an acquirer to pay every shareholder the same price, i.e. the highest price at which the share can be acquired.
Super majority rule: An acquirer is required to obtain more than a majority of votes to replace the board.
Litigation: Management can delay a potential takeover in courts if the potential acquirer is in the same industry, in which case antitrust litigation issues come into play.
Staggered board is the most effective preventive takeover strategy. It is described below:
Each year only a fraction of directors appear for reelection. In this way, it can be ensured that on the day of the annual shareholders meeting, no one can take complete control of the board. One-third of the board is replaced and two-thirds remain in office. So, the company will continue to be in control of the existing board at least for one year, during which a lot of harm can be done. Refinement in defensive weaponry is one of the reasons why hostile takeovers declined after 1990s.
The Indirect Effects of (the Possibilities of) Attack and Defense
There is a managerial factor that provides a dull resistance and makes the value look reducing. Let us look at an example to understand this in a better way. The resistance that you have started on with cans start by targeting the extent. There is a greater impact that is created on the shareholders and they raise all the prices. The forced and acquired form is made in a simple form. The requites are very good and smooth with their disposal methods.
This will make the legal team very friendly to the investor team, forming a golden parachute – this is the form of personal bribery. The management is of a free solution and the shareholders are mostly in the compassing of the solution. This is what the main source claims at least. If the shareholder team is not a very big one, there is a definite chance of the value and the target value is gotten and awarded.
This will not be a clear charge in the most abundant form. Hence there is a need for many layoff and compline. This is a grandeur opportunity for all the brands to flourish and make a stagnant value worth from the market. The targets are often made the center of all repercussions and the solutions are all sent in for negotiations. There is a whole some change in the way the market value is distributed. Target is hence better fetched and made an anomaly of.
23.3 C Proxy Context and Shareholder Resolutions
A proxy context is defined as a situation where a large shareholder can solicit other shareholders to vote against the current management and to favor the board of new members. A hostile offer and a proxy context is launched by a hostile would-be acquirer so that he can purchase all the shares. In a shareholder proposal, any shareholder can put up a proposal where every shareholder would cast his/her vote. The SEC would judge whether the proposal would be accepted or not. Therefore shareholder proposals are not binding.
23.3 D More Empirical Evidence about M & A Activity
Looking at the systematic empirical evidence is an easy deal but having fun with the things that you have in your hand is much easier to consider. So, looking at an example,
The chief of yahoo Jerry yang made a plan to make the company take a stupendous start on every page that the internet can use. However he failed in the very attempt of doing so and thus the entire solution to an end.
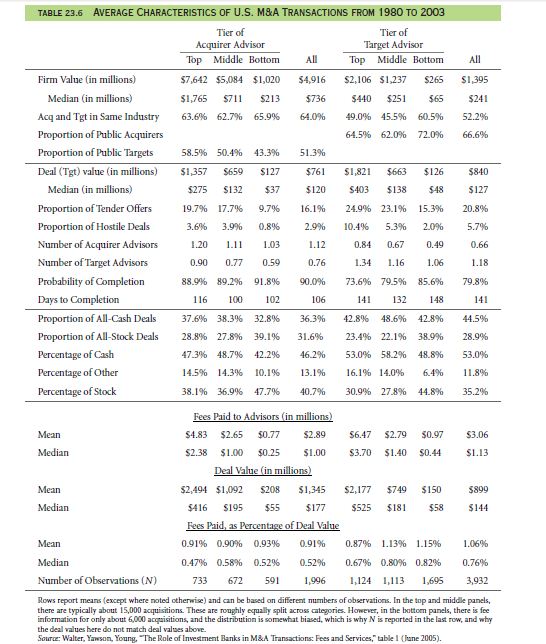
More about Takeover Characteristics and the Role of Investment Banks
Clean capital structure, debt refinance, and geographic proximity, clean operation history of enhancing shareholder values, experienced management, minimal litigation risks, expandable margins and solid distribution network are the factors on which takeover characteristics depend. Acquisitions are of two types. If the acquirer pays by cash, it is cash offer or if it is paid by using the corporate’s share as currency, it is called a stock offer. If a merger which is taking place is hostile, a larger portion of the targets engage top-tier advisors.
The data that is given suggests that there is a chance to use the main techniques that we learned in the other chapters along with what I just explained. The total M&A value that is given and requested on the validation point is the subject makers. The main thing that needs to be used in this case is that there will be a future validation that uses all the stocks and bonds that are needed. The success of the entire 1/3rd of the capital can be recurred and gotten value of.
SUMMARY
This chapter covers the major points which are discussed below:
Investment banking consists of services such as underwriting and advisory services. Some investment banks are engaged in other non-investment-banking services such as proprietary trading and asset management.
Nowadays, securities underwriting is primarily the facilitation of public offerings facilitate securities underwriting.
Advisory services are about the facilitation of mergers & acquisitions.
The investment banking market is an agent market which is different from commercial banking where loans are made by the bank.
The equity capital markets of the United States, Europe, and Asia are about
equal in terms of equity size. The debt market of U.S. is larger than that of Europe or Asia.
The U.S. investment banks are at the top because of their ability to attract the best talent from all over the world and as a result, commercial banking is more diffused here.
No investment bank has a share of more than more than 10% in the market.
In equity underwriting, securities are riskier, and due diligence and placement are difficult. Therefore, it is more profitable than debt underwriting.
Though hostile acquisitions are rare, yet they are important because they set the stage for managerial behavior.
Competitive bidding results in lower underwriter spreads.
Characteristics of underwriter spreads: A strong relation between the offering size and the underwriter spread for equity offerings. There is no relation between underwriter spread and offering size for debt offerings.
Larger SEOs have lower spreads.
M&As can create shareholder value with the help of scale synergies, reducing competition, providing expertise, eliminating poor management, shutdown efficiencies, better corporate governance, stakeholder expropriation of stakeholders and tax benefits. If governance and operations become worse, the values will be destroyed.
Value gains benefit target shareholders and not managers. Most of the time acquiring managers tend to overpay for targets.
Target management can resist acquisitions through greenmail, target acquisitions, scorched earth strategies, poison pills, new share issues, provision of fair value, rules of super majority, litigation, and staggered boards.
Even though shareholder resolutions are cheaper, not binding and nudge the management into doing the right thing.
Key terms
Acquisition
Black knight
Book runner
Bridge financing
Cash offer
Core equity
Corporate raider
Due diligence
Glass-Steagall Act of 1933
Golden parachute
Hostile acquisition
LBO
Lead manager
Leveraged buyout
Management buyout
MBO
Merger
Origination
Placement
Private equity
Proxy contest
Rollup
Shareholder proposal
Shark repellent
Stock offer
Syndicate
Tender offer
Tombstone
Underwriter
Underwriting
Unsolicited bid
White knight
PROBLEMS
What is the importance of guarantee of securities placement success which are provided by underwriters to their clients?
List the important services and functions of underwriters.
State the functions of M&A advisory services.
What is the process by which client assets under management and Tier 1 capital translate into market value? Are U.S. and U.K. banks relatively more valuable than their foreign competitors? Justify your answer.
What is the importance of American market in equity underwriting over European market?
What is the link between underwriting and M&A linked?
Check the link http://www.thomsonreuters.com/products_services/financial/league_tables and find the top debt underwriters, equity underwriters, and M&A advisors of this year.
Are hostile takeovers rare?
What is the difference between the interests of investment banks and their clients?
What is the main institutional difference between equity issues by regulated utilities firms and those issues by non-regulated ordinary firms? Which of them two raises capital at a cheaper rate?
Are competitive bids for underwriting services more expensive than non-competitive bids?
Go through the financial websites to determine what were the biggest three acquisitions in the last 12 months.
Search about Cerberus Capital’s portfolio companies on the internet. When were the companies taken over? Did the interest rates affect Cerberus’s takeover activities?
List the main sources of value generation in mergers and acquisitions.
What are the strongest sources of value in an acquisition in leveraged buyouts? How are they different from ordinary acquisitions?
Do acquiring or target shareholders gain more from the acquisition? Or is it that acquiring or target management gain more from an acquisition?
What is the most effective anti-takeover device? Explain its working. What are the steps which a raider should follow to take over a company that has deployed this device?
Are golden parachutes always/never in the interest of shareholders? Explain your answer giving reasons.
Should long-standing workers who lose their jobs also deserve and receive golden parachutes?
What is the form of payment received by the shareholders of the target firm when one firm acquires another?
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction of corporate finance
- The time value of money and net present value
- Stock and bond valuation annuities and perpetuities
- A first encounter with capital budgeting rules
- Working with time varying rates of return
- Uncertainty default and risk
- Risk and return risk aversion in a perfect market
- Investor choice risk and reward
- The capital asset pricing model
- Market imperfections
- Perfect and efficient markets and classical and behavioral finance
- Capital budgeting applications and pitfalls
- From financial statements to economic cash flows
- Valuation comparables financial ratios
- Corporate claims
- Capital structure and capital budgeting in a perfect market
- The weighted cost of capital and adjusted present value in an imperfect market with taxes
- What matters
- Equity payouts
- For value financial structure and corporate strategy analysis
- Capital structure dynamics firm scale
- Capital structure patterns in the united states
- Investment banking and mergers and acquisitions
- Investment banking and mergers and acquisitions
Links of Next Financial Accounting Topics:-