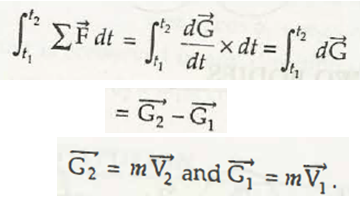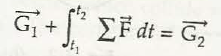Linear Impulse can be defined as the equivalent change in linear momentum in the same direction. The S.I. unit of Linear Impulse is Newton-second (N-s).
Let us consider force acting on the body be
Linear momentum can be given by,
dt
Suppose the force acts on the body between separate interval of time t1 and t2. Now, linear momentum can be given by,
It can be modified as,
= dt
= 2 – 1
Where,
2= m 2
1 = m 1
Components of Linear Impulse
Considering the components of linear impulse, it consists of x, y and z components. These are written as-
xdt = m x2 – m x1
ydt = m y2 – m y1
zdt = m z2 – m z1
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Position vector velocity and acceleration
- Plane kinematics of rigid bodies introduction
- Combined motion of translation and rotation
- Rectilinear motion in kinetics of particles
- Work and energy
- Linear momentum
- Linear impulse
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-
- Conservation of linear momentum
- Direct collision of two bodies
- Oblique collision bodies
- Coefficient of restitution
- Force mass acceleration
- Simple stress introduction
- Normal strain
- Statically indeterminate system
- Introduction to thermodynamics
- Statement of zeroth law of thermodynamics with explanation