Contingency Theory of Leadership
There are lot of stories that are heard in the corporate world about failures of leaders because all of them have failed to know on what sector or purpose they are working on. Here in this chapter it is explained 3 chief contingency theories. They are Fiedler, path goal and Hersey- Blanchard. Each of them has different concept of leadership style & features & also attempts to clarify the if and then contingencies. It means on the basis of situations which leadership style will be appropriate.
The Fiedler Model
Fred Fiedler developed the 1st contingency leadership model in the history. This mode is based on certain concepts. It has proposed that the effective performance of group is complete depended on the leadership style and the situation it is placed in and how much the leader can control the situation. This model tells that there has to be a certain kind of leadership style which would match up with every situation at a time. Its key was to 1) identifying a particular situation and style 2) defining leadership styles & different kinds of situations.
Fiedler said that to become a true successful leader and then give success to the firm requires a particular kind of leadership styles that can be task oriented or may be relationship oriented. So as to measure this leadership style and identify it he made LPC questionnaire. These questions contain about eighteen pair of adjectives that are contrasting. Examples are hot cold, pleasant unpleasant, friendly unfriendly, boring interesting etc. Now respondents were basically asked to rank the co-workers with in the scale of one to eight and rank them on the basis of the 18 adjectives. They have to mention the person with whom they have least enjoyed with and most enjoyed in the ranking system.
If here the leader described the preferably least preferred worker in positive terms then this respondent is primarily interested in better personal relationships with the co workers& this style can be described as relationship oriented style. On the other hand if you see the least preferred worker in rather unfavourable term you will be primarily interest in productivity & getting down the job. So your style can be labelled as the task oriented one.
Fiedler on the other hand acknowledged that a little no of people might can fall in between the 2 extremes and not have any cut dry leadership styles. Other thing that Fiedler observed that that leadership style of a person is not fixed that is the style is fixed for every situation. Whether you are a task oriented or relationship oriented your nature will be same in all situations.
After the leadership style of the was assessed through LPC its time to evaluate situation in which the leadership style is going to work. Fiedler’s Leadership research uncovered the 3 contingency dimensions which defines key situational factors in the leadership effectiveness.
Following are the 3:
- Leadership member’s relation: this is the degree of respect, trust and confidence that the employees have towards the leader; this rated as poor or good.
- Task structure: degree at which job assignment were structured and formalized. Either low or high.
- Position Power: degree of the influence that leaders have over the activities like hiring, discipline, firing, promotions & salary increase. This is also rated as strong to weak.
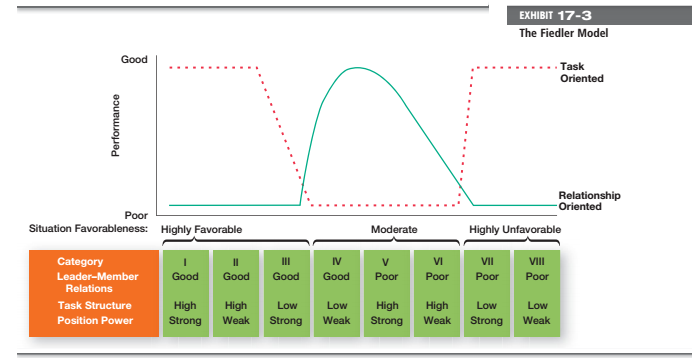
As Fiedler managed to describe the situational variables and leadership style variable he has everything given that are needed for defining specific contingency on leadership effectiveness. So to do that he has studied over 1200 groups to compare the relationship and task oriented styles which falls under the 8 situational categories. What his theory said is that the task oriented ones are successful in both favourable and unfavourable situations no matter what happens. See Exhibit 7.3. In contrast to this relationship oriented leader performed much better in the moderately favourable situations.
As Fiedler has said that the leadership style of individuals remains fixed in every situations there are only 2 ways that could increase leadership effectiveness. One can be by bringing any new leader whose style suits the situation that has occurred there. Such as if the situation of the group is too unfavourable but is managed by a relationship oriented one he must be replaced by a task oriented one to deal with the unfavourable situation.
The other thing can be by changing the situations so as to suit the leadership style. This can be done by increasing and decreasing the power which leaders have such as granting, promotions, firing, hiking in salaries, maintaining discipline or by restructuring the tasks performed. This can also be done by improving leader member relations.
Hersey & Blanchard’s Situational Leadership
Hersey and Blanchard had been successful in developing a leadership theory which has already gained strong following among the management development specialist. On this model this is known as situational leadership or SLT theory which mainly focuses on followers readiness. 2 points needs to be clarified before we move further. What is the meaning of the term readiness & why leadership theories are focusing on followers?
This emphasis on followers of the leaders tells that the role of the followers in effective leadership. It is the followers who accepts or rejects the leader, so the leadership effectiveness continuously depends on the followers. The effectiveness of the group completely depends on the followers. These important dimensions are often been overlooked in most of the leadership theories. Readiness can be defined as the extend at which people have willingness and ability to accomplish any specific task.
SLT has identified the same leadership dimensions which Fiedler has already identified: relationship and task behaviours. They are being evaluated with high or low factors. Then they re combined in 4 leadership styles that are described in the following:
- Telling: here the leaders defines the roles & tells people what & when they where to do different tasks.
- Selling: here the leaders have provided both the supportive & directive behaviours.
- Participating: here the leader and the employees share in the decision making process. Here communication and facilitating is a great factor that needs to be considered.
- Delegating: here the leader provide little support and help.
The final part of the component in this model are the 4 stages of the follower readiness:
- R1: here people are unable and unwilling to do something or taking any kind of responsibility. Followers are not confident and competent.
- R2: people are being unable to do necessary jobs and works. Here the followers are being motivated and are doing inappropriate works which lacks skills.
- R3: people do not want to follow their leaders but they are able to do work. Followers are able but do not want to perform the task.
- R4: People are willing to do and are also able to work what is given to them.
SLT basically is trying to make the readers understand that this is a father and child relationship. As the child becomes mature fathers needs to relinquish the control on child. It is that simple. As the followers are reaching higher level of readiness here the leaders response not just by decreasing the control on the activities they do but then they again decrease the leadership behaviours. What it says is that the leader has to be both willing to do the work and make his employees do the same.
Performing ay one often two will not do the work. Leaders have to be responsible to work accordingly and maintain the readiness of the workers. SLT repeatedly emphasizes on the fact that the readiness of the followers and their respect and trust towards the leaders is a must. Without which no work is going to be successful. SLT says it needs attention on every detail of the followers and hence to become a successful leader the reaction of the followers is very important.
Path Goal Model
There is other approach to get know the leadership theory that is the path goal theory. This approach is based on certain rules and terms. This states that the duty of a leader is to assist his followers to achieve their goals and give them every help they need to achieve that goal. They have to ensure that these goals are compatible with the actual goals of the organisation.
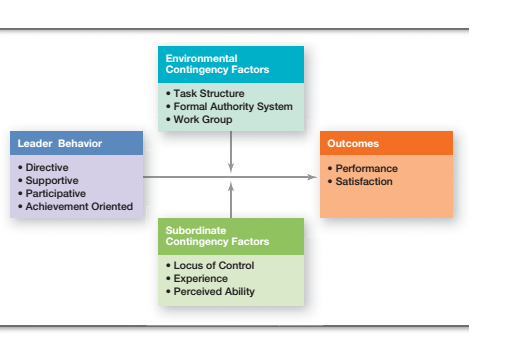
Path goal theory is the replica of the theory on motivation. Robert House developed this goal. This goal theory states that leaders have the responsibility to clear the path through which the followers have to go through. Rather all the obstacles of achieving the goals needs to cleared by the; leaders so that the followers can straight move towards their goals. This will help the followers to achieve their goals.
Robert has identified the chief 4 leadership behaviours:
- Directive Leaders
- Supportive Leaders
- Participative leaders
- Achievement oriented leaders
This theory is a complete contrast to Fiedler’s view. Robert says that a leader can change his/her behaviour or style in different situations and can change his behaviour according to the situational factors. This is quiet opposite to what Fiedler has said.
- Directive leadership has greater satisfaction when tasks when the tasks is stressful or ambiguous than highly structures & will lie out. As the followers are not sure about what they can do they will needed to be directed by the leaders.
- Supportive leadership sometimes results to good employee performances and good management returns as they are supported in case of structured tasks. Here support is the main thing that is needed in such tasks direction is not needed.
- In cased of directive leadership followers are able enough to take their own decisions. Here they are not needed to tell what to do.
- The more there will be communication between the leaders and the employee the more will be the effectiveness of leadership. So here the leaders’ role s simply to support the employees and maintain good relationship.
- Directive leadership makes high employee satisfaction as there will be substantive conflict in a work group. Here the followers need leaders who have the ability to take charge.
- Subordinates with internal locus control become more satisfied in participating style. As these followers thinks that they can control the working of the firm they takes direct participation there.
- Subordinates having external locus control are more satisfied by directive style. As they believe that whatever happens is due to the force of external environment they need a leader who can assist them in what they can do.
- Achievement oriented leaders will increase the subordinates expectancy that effort leads to higher performance whenever the tasks becomes ambiguously structured. Here setting challenging aims are important so that followers know what actually they will have to perform.
There are mixed support of the path goal model. We can make it short. An employee’s satisfaction and performance are always positively influenced in when the leaders choose a particular leadership style which compensates for short coming in either employee or work setting. What is noteworthy is that if the leaders try to explain tasks and direct term on tasks that are already known or clear by the employees, the employees might find it insulting or redundant if the leaders do so. Thus this theory is completely based on the behaviours of the followers towards the leaders.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Managing human resources
- Managing teams
- Understanding individual behavior
- Managers and communication
- What is motivation
- Managers as leaders
- Who are leaders and what is leadership
Links of Next Fundamentals of Management Topics:-