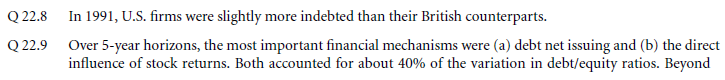It is not possible to believe what they say because CFOs motives that they declare publicly might not be always be what their actual behind the door motives are. Harvey along with Graham back on 2001 conducted an examination to understand how their declaration drives their equity issues and debt issues. Both of them inferred something really exciting and puzzling at the same time.
Firstly, you must know CFOs are not bothered about the benefits from tax against debt in Corporate Sector. They are very much bothered regarding the ratings of credit. Management may be conscious about the foundation of trade off along with the distress of financial conditions.
A lot of arguments of capital set up is already present and they seem to have to base to managers keeping their personal motive in mind from income taxes which are like a burden to the shoulders of the stake holders, in order to focus on all creditors that they have to market product strategy and taking into consideration certain factors, to keep an eye on the financial flows, the calculated announcement of confidential information to cost of transaction contemplation. Firstly, it might not have bad effects as you may think it will. There are chances managers will pay heed to all the above mentioned points, as the capital costing will mirror itself through all the considerations. Take an example; if an investor of the firm faces higher tax repercussions, it will increase the firm’s capital costing and by now you know how bothered managers are about their capital expenditure. Secondly, entities without needing cash hike; then managers might not calculate the proper obstacle against their venture. The obstacle rate could be really high or really for a particular project.
- Managers prefer a little “financial flexibility” and this resembles to the preference of having cash flowing around them also unrecorded which actually makes a lot of wit from the point of view of the Management but it is a heads up to the fact that flow of cash is the real issue. The affinity of managers towards such flexibility is because they have a hidden intention to surpass rival companies. This step will not churn value for the concerned firms’ shareholders. With near to negligible in numerous companies that have a good foothold. But the fear of scarcity of note is a grave issue behind the demand of flexibility which is unlikely.
- Managers are weary of small percentages of profit shares on issuance of equity is more than required. It does not make much sense because recent fund raiser will obviously produce earnings.
- The managers who put forward claims to aim at debt ratios have a tendency to include the equity when it shows a recent increase in its value, and also have a tendency that faced a recent downfall. This is important as it is strongly recommended to calculate the ratio of debt to equity.
- The Management has a stern belief on their credibility of manipulating movements of financial market.
- Almost two parts out of three of the entire population of managers gauges the exchange market trivializes their firm and this is the reason why a lot of them refrain from equity issuance. If the Company shares experience a recent increase, they feel there is a “window of opportunity” to sell shares.
- They have a tendency of issuing more debt when interest rates face a downfall. You will surprise to know that though it might seem unreal to believe that they have a collective ability to influence the market timings. To give a believable explanation of behavioral finance.
These firms have a firm belief that dividends have a tendency to draw more individual shareholders from retail exempting big companies tax-exempted vectors. So, in this case it can be said that investors are wrong in decision making, in case the Management is right.
SOLVE NOW! SOLUTIONS
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction of corporate finance
- The time value of money and net present value
- Stock and bond valuation annuities and perpetuities
- A first encounter with capital budgeting rules
- Working with time varying rates of return
- Uncertainty default and risk
- Risk and return risk aversion in a perfect market
- Investor choice risk and reward
- The capital asset pricing model
- Market imperfections
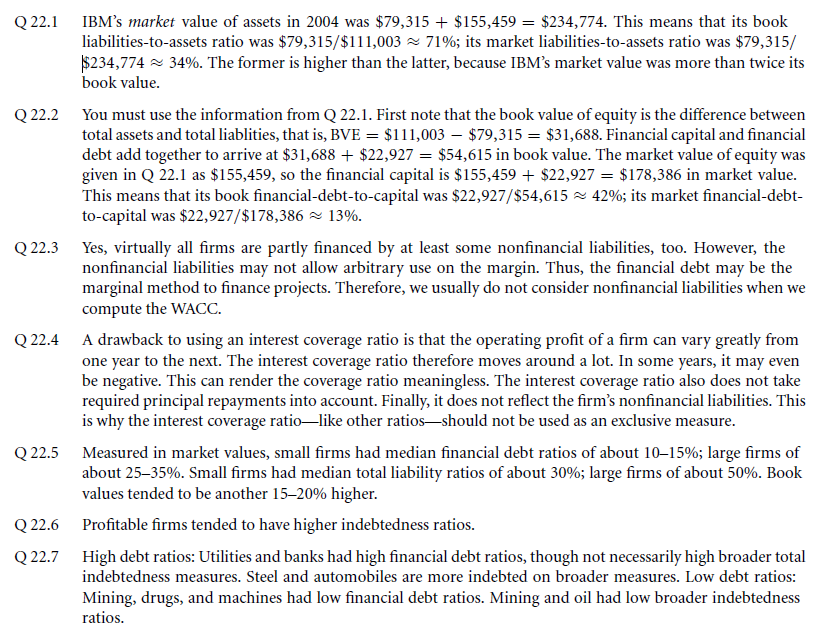
- Capital structure patterns in the united states
- Empirical capital structure patterns
- Mechanisms versus causes
- What are the underlying rationales for capital structure changes
Links of Next Financial Accounting Topics:-