Sliding vector explains the action of a vector on a rigid body. A vector is said to be a sliding vector when it gets replaced by any other vector having the same direction in the same magnitude. The transmissibility of the forces, “If a force, acting at a point on rigid body is lifted to any other point which is on the line of action of the force, the external effect of the force on the body remains unchanged.”
It means the motion and equilibrium of the rigid body should get a proper disturbance. Only in that case a vector is called a sliding vector.
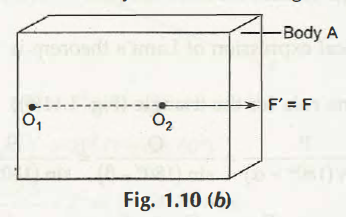
You can easily understand with the given figure in which a rigid body A gets the action of vector F’ replaces the same magnitude F. According to this principle as well as according to the definition of sliding action, F gets shifted from point O1 to O2.
The complete line of action on the rigid body is a single line of action. So, anyone can easily grab the solution of sliding vector by understanding the fact or the theory in a proper way. It is also important to understand that line of actions takes place in the different points.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Introduction to statics
- Idealizations of mechanics
- Laws of mechanics
- The law of parallelogram
- Types of forces
- Coplanar collinear
- Coplanar concurrent
- Coplanar parallel forces
- Coplanar non concurrent and non parallel
Links of Next Mechanical Engineering Topics:-