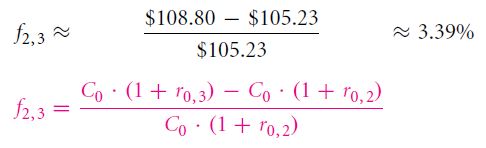The yield curve can be used for contracting a loan in the present with an interest rate of 1% which will begin in two years. This is done when you want to finance a project today which requires cash outlays in the next two years and pays off the cash after the investment has been made. This is called locking in the forward arte which is dependent on the yield curve of today. The transaction in this case is called the forward transaction.
Computing and locking rates are immensely important for bond traders. Forward arte is applicable for future cash investments.
Let us know understand short sale by using an example. Treasury bonds can be bought and sold without actually owning them. This can be done by borrowing Treasury Securities and selling them to a third party. The cash which is received can be used to buy the bonds and then return them to the lender of the Treasury Securities. Short selling allows you to issue a security, receive money and then return it to the lender with an appropriate interest. If you are selling a $91,915.15 3 year Treasury note with interest rate of 2.85%, you will get $91,915.15 at present in the form of cash but you will be required to pay $100,000 as repayment in the next 3 years. Selling a Treasury short can be considered as a sort of borrowing money. In the real world, these transactions are performed by a broker.
When you are holding a security, it is speculated that the price will go up and when you are selling a financial instrument, it is speculated that the prices will go down. If the price of the Treasury note goes down to $50,000, you can then purchase the note for $50,000 and repay some part of the $100,000 which you had to pay when you earned $91,915.15 and you will still make a profit of $41,000.15. You also have the option of returning the Treasury to the lender. But if the price of the Treasury note goes to $99,000 then you suffer a loss of $7,084.85.
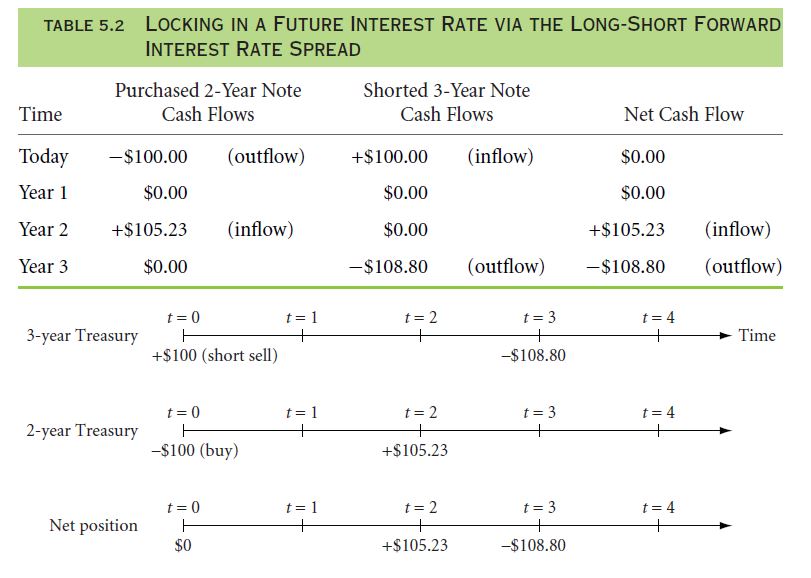
Let us now study two simultaneous transactions. You bought 2-year treasury notes at an interest rate of 2.85% and sold a 3-year Treasury note at the same interest rate. For every $100 you borrow, the transaction will result in an inflow of $108.80 in 3 years and for buying the note, you would invest $100 and you will be able to earn $105.23 in two years.
The details of the transaction have been presented in the table:
The interest rate of the transaction can be given as:
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Working with time varying rates of return
- Inflation
- Study of treasury bills and yield curve in time varying interest rates
- Why is the slope of yield curve upward
- Corporate insights about time varying costs of capital obtained from the yield curve
- Extracting forward interest rates
Links of Next Financial Accounting Topics:-