Practice sessions
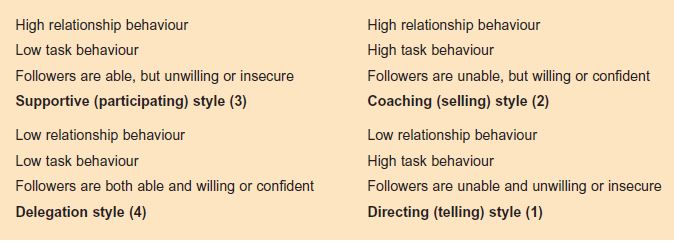
Leadership behavior is explained based on the concepts that are based on that of production-centered and people-centered behavior. A model developed by Hersey & Blanchard in 1988 identified that leadership behavior depends on situation. Leaders need to adapt to various styles in order to meet all the budding demands of the environment. Ability along with willingness are the two criteria on which the leadership qualities are measured. Level of all ability includes knowledge, skills and experience which needs to be present in the individual to deal with the task at hand, the other one is willingness, where factors such as motivation, commitment and self-confidence plays a role. The 2 dimensions of leadership behavior are task behavior and relationship behavior. Task behavior is directive and relationship behavior is supportive. Task behavior is about what leaders tell the team members to do. It is more of a one-way process. On the significant other hand, all sort of relationship behavior is about the interaction between the leaders and the members. It is a two-way process. It includes, facilitating, supporting and listening behavior. These two behavioral aspects are represented by a 2-by-two matrix shown below:
In 1967, Fielder presented another contingency theory, where leadership behavior depends on three factors. First is the nature of the main relationship is that which is in between the leaders and the team members, second is the structure of the task and the third is the position and power of the leader.
In 2000, Goleman made a report where six different leadership styles were identified. But, practically it has been found out that leaders depict a combination of these styles. These six styles are linked with emotional intelligence &leaders always must understand the situation where these styles can be used. Here is the list of leadership styles given by Goleman.

Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Strategic aspects of performance
- Organisational performance
- Individual performance management
- Team performance
- Introduction leadership and motivation
- Leadership and management
Links of Next HR Management Topics:-
- Do leaders need different styles for different situations
- Do we really need heroes
- Leadership and motivation summary propositions and general discussion topics
- Managing absence and attendance
- Interactive skill 3 appraisal interviewing
- Strategic aspects of development
- Context competence competencies
- Learning and development