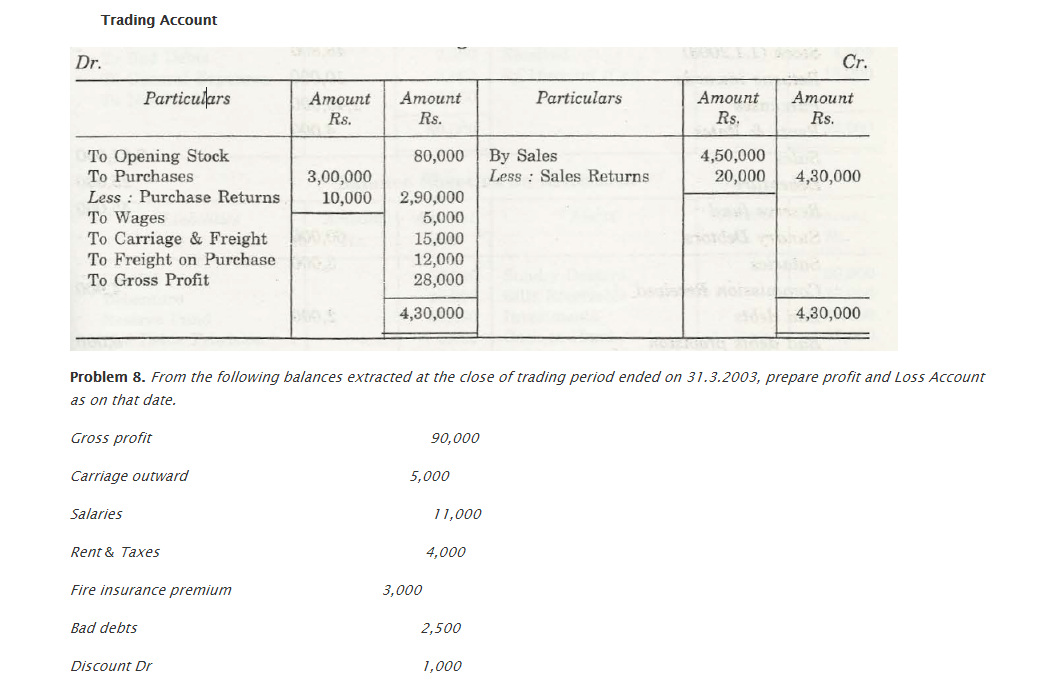
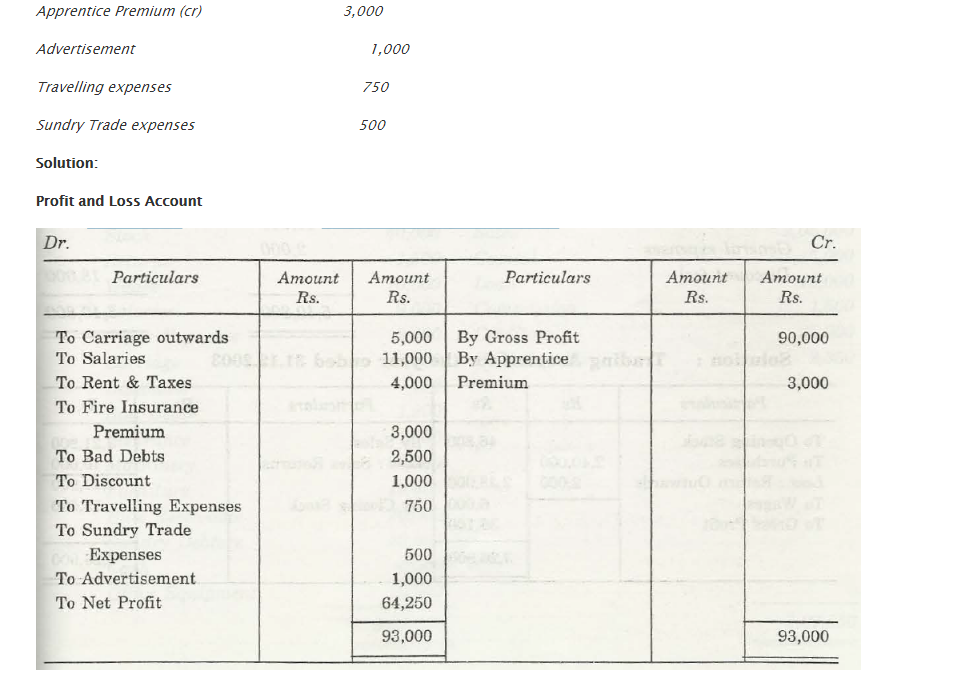
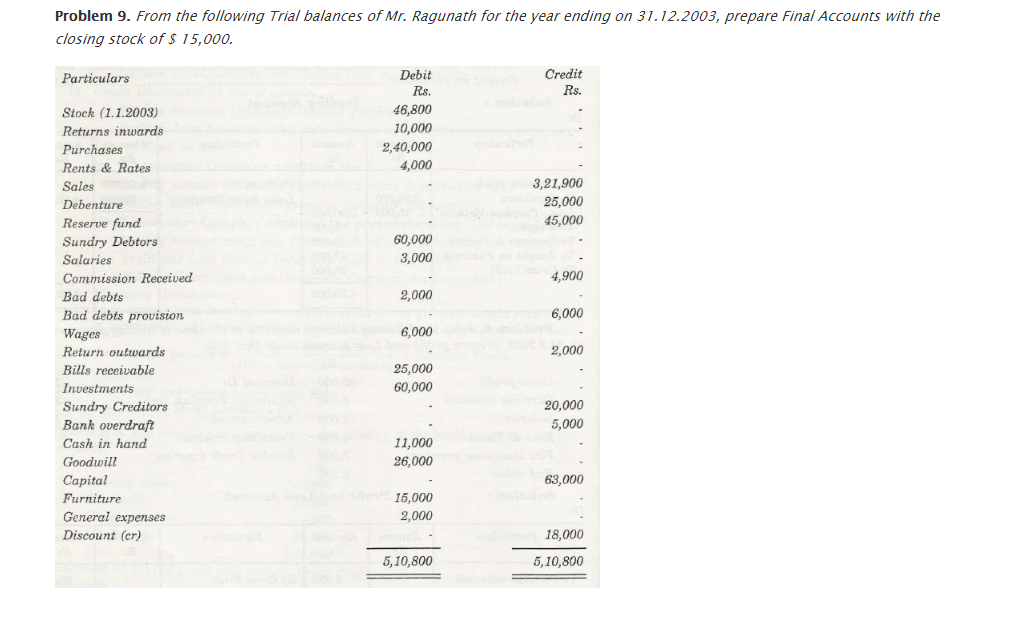
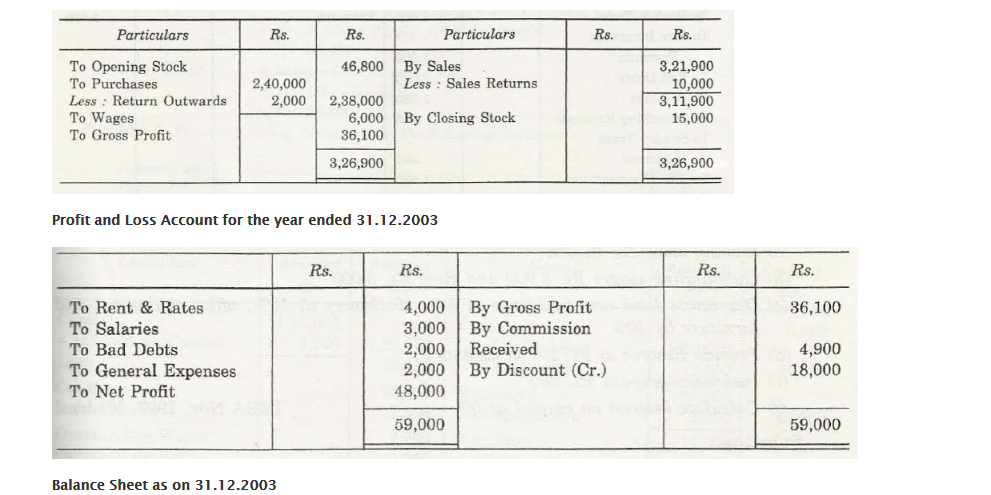
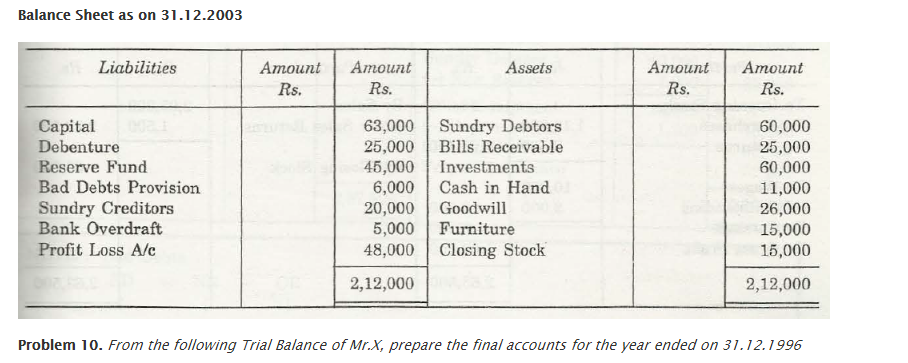
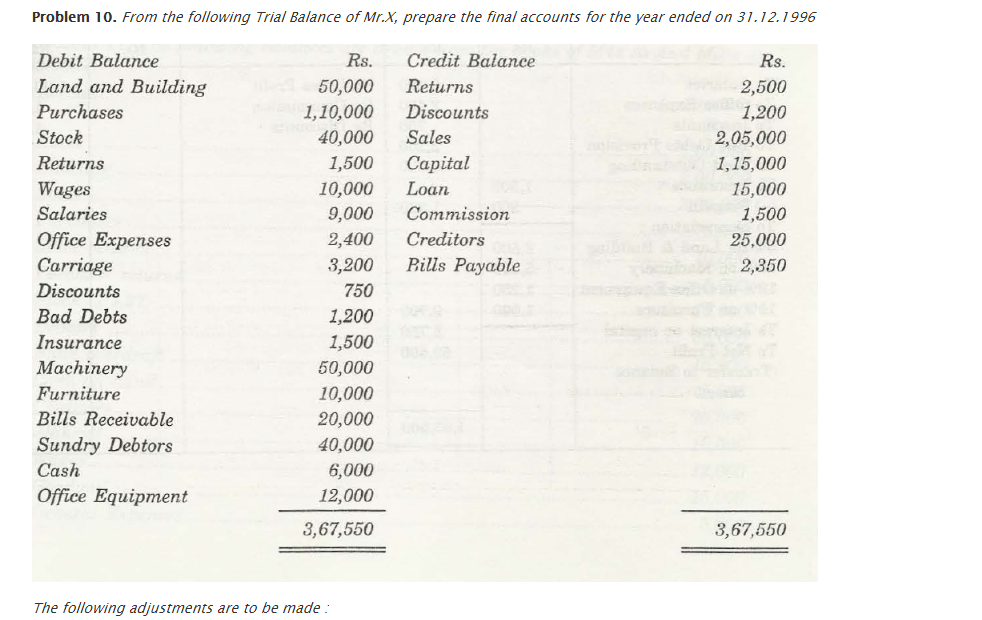
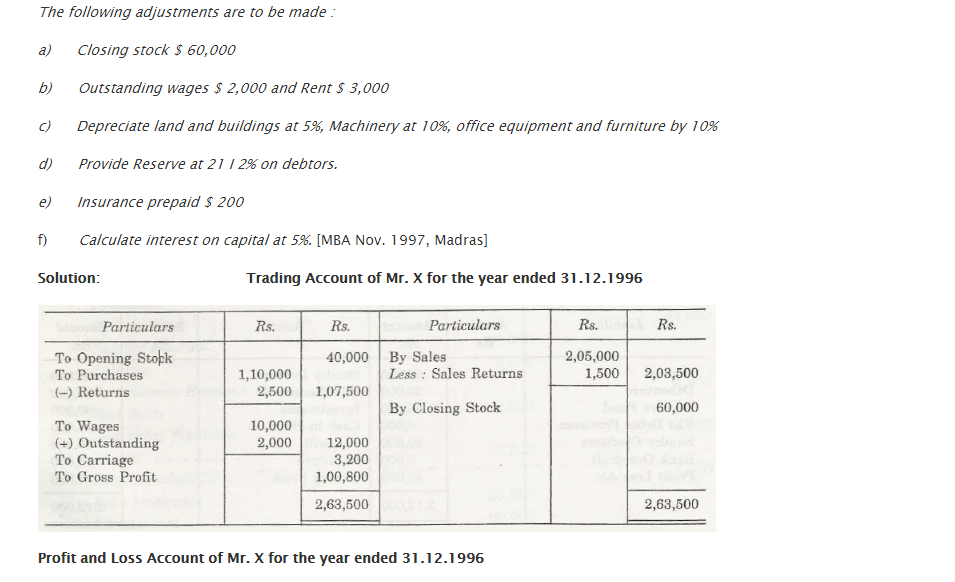
For any business organization, it is important that they have a suitable financial statement that would depict profit and loss that is faced by that company. The Trading and Profit and Loss Account depicts the total amount of profit and loss that is associated with any company. Also, with help of Trial Balance, a company will be able to check out what is the financial position of that company in comparison to others of the same zone.
There are certain entries that are found at the end of accounting period known as adjustment entries, and total net profit can be obtained only after adjusting outstanding expenses and pending bills.
Adjustments to be made at an annual level:
- Prepaid expenses
- Outstanding expenses
- Accrued income
- Closing stock
- Depreciation
- Income received in advance
- Interest on drawings
- Interest on capital
- Provision for bad and doubtful debts
- Bad debts
- Interest on loan
- Free sample goods
- Provision for discount on debtors
- Provisions for discount on creditors
- Goods lost due to fire or any other untoward incident.
In case of adjustments, there are two important things to note, since certain adjustments are made beyond Trial Balance.
- Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet
- Trading Account and Balance Sheet
Treatment of Adjustments:
- In case of Closing Stock, Balance Sheet is on Asset side, and Trading Account is on Credit
- In case of Outstanding Expenses, Trading or Profit and Loss Account is on Debit side and Balance sheet is on Liability side.
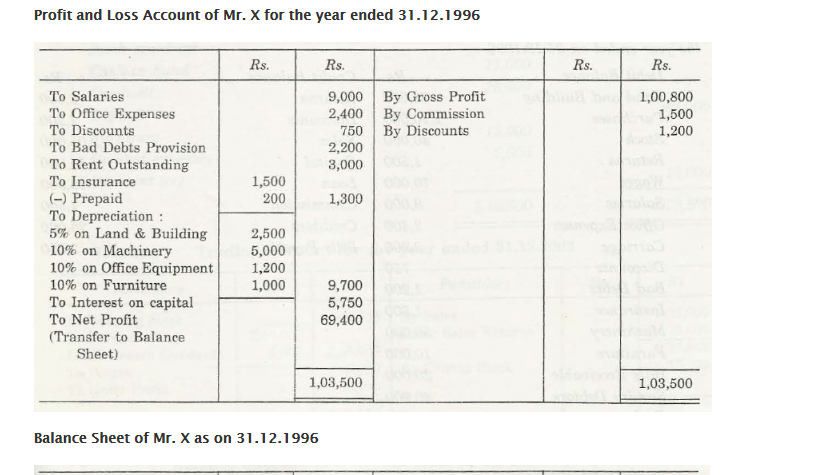
- For Prepaid Expenses, Balance Sheet is on Asset side, and Profit and Loss Account is on Credit
- For that Income which has not been received, Profit and Loss Account is on Creditside, and Balance sheet is on Asset side.
- In case of Depreciation, Profit and Loss Account is on Debit side while Balance Sheet is on Liability side.
- In case of Advance Income, Balance Sheet is on Liability side while Profit and Loss Account is on Credit
- Interest on Drawings shows Profit and Loss Account on Credit side, while Balance Sheet on Liability side.
- For Interest on Capital, it can be noted that Balance Sheet is to be placed on Liability Side and Profit and Loss on Account Debit side.
- For Bad Debts, Profit and Loss Account is to be presented on Debit side and Asset side will have Balance Sheet.
- For getting Interest on Loan, Liability side will have Balance Sheet while Debit side will have Profit and Loss Account.
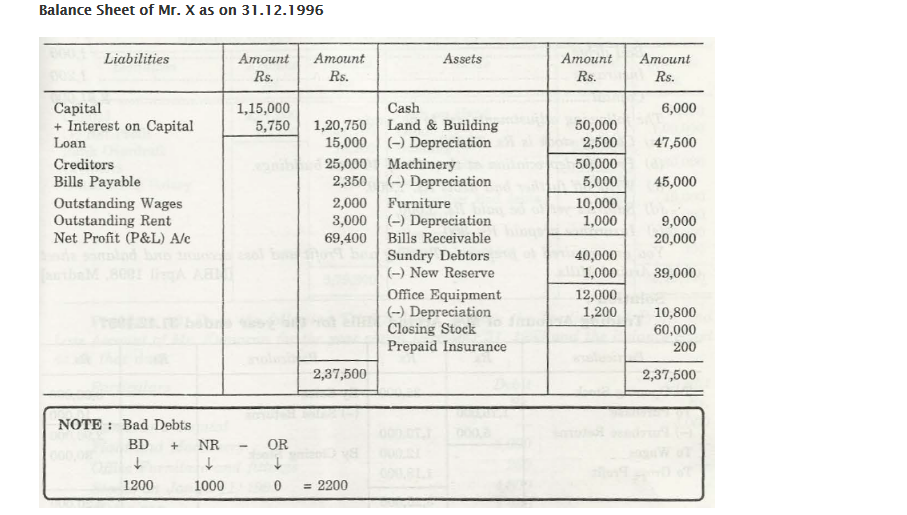
In case Bad Debts are considered, the formula that is to be applied is:
BD + NR- OR where Bad Debts should either be given Trial Balance of Adjustments, or at times both. The value that is calculated can be transferred on either side of the account.
- For Provision of Discount on Creditors, Credit side has Profit and Loss Account with Balance Sheet being placed on Liability side.
- In case of Provision of Discount on Debtors, Debit side has Profit and Loss Accounts, and Asset side has Balance sheet.
- For those goods that are lost due to fire or any such untoward incident, with Insurance Company admitting complete claim, Trading Account is on Credit side while Balance sheet is on Asset side.
In case Insurance Company admitted only part of the claim, complete Trading account on credit side while close to 40% on Debit side for Profit and Loss Account.
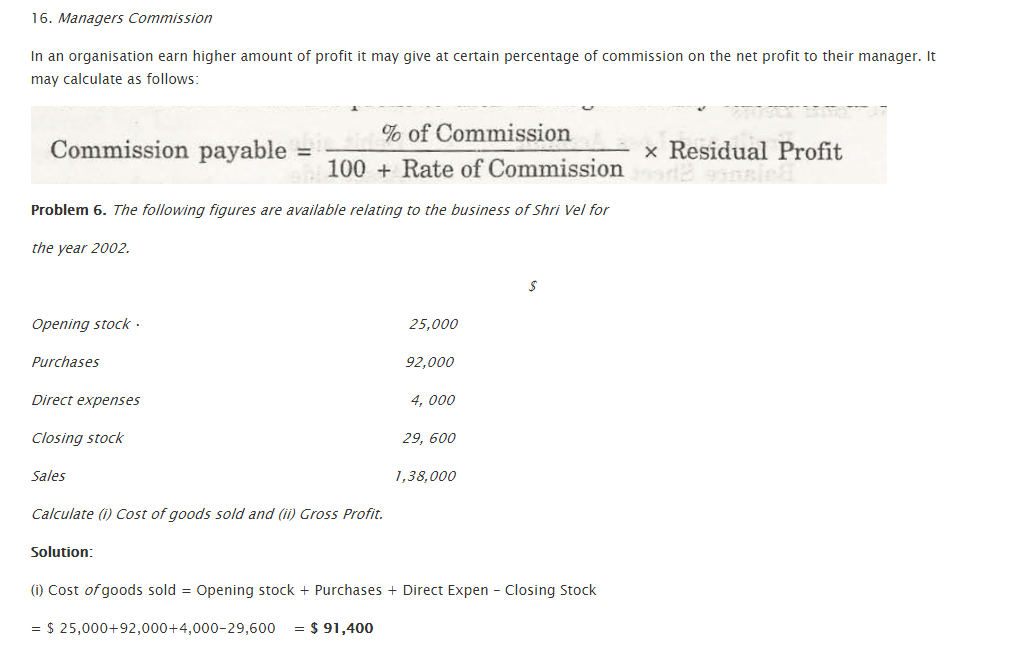
- To find Manager’s Commission, certain details are to be placed. The formula is:
Payable Commission = (Commission percentage/100+ Rate of Commission)/Residual Profit
It is based on this chart that further problems are solved.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
Links of Next Finance Topics:-
- Introduction of fund flow statement
- Introduction cash flow statement
- Ratio analysis significance of ratio analysis
- Fixed assets and depreciation meaning causes objectives methods and basic factor
- Cost accounting concept objectives advantages limitations general principles and cost sheet
- Job costing
- Introduction process costing
- Activity based costing introduction concept and classification
- Introduction inventory pricing and valuation
- Standard costing introduction
- Management accounting
- Marginal costing
- Relevant cost for decision making
- Budget and budgetary control
- Limitations of historical accounting
- Introduction to responsibility accounting
- Introduction to financial management
- Introduction and types of dividend
- Concept of cost of capital
- Capitalization meaning
- Concepts of working capital
- Concept of capital expenditure
- Learning objectives and chapter outline
- Limitations of operations research
- Linear programming learning objectives and outline of chapter
- Introduction learning objectives
- Duality in linear programming
- Learning objectives
- Learning objectives and chapter outline in assignment model
- Minimization problems
- Learning objectives the transportation problems
- Special case of traveling sales man problem
- Replacement theory learning objectives and chapter outline
- Learning objectives and chapter outline for waiting line queuing theory