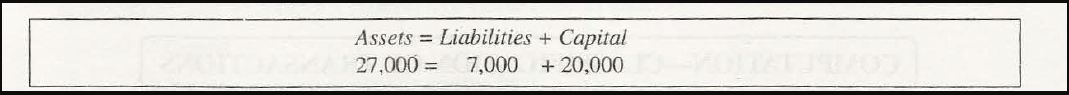The three primary elements of any business transaction are- assets, liabilities and capital. This relation between them in Accounting Equation remains unchanged no matter how worse or good the situation of a company is. It has even been justified by mathematical data.
Inter-relationship of these three accounting terminologies- assets, liabilities and capital, results into nine transactions. These transactions depict that a change in one element will automatically lead to a corresponding change in all other elements. These nine business transactions are as follows-
- Increase and decrease in liabilities
- Increase in assets with a corresponding increase in liabilities
- Decrease in assets with a corresponding decrease in liabilities
- Increase in capital and decrease in liabilities
- Increase and decrease in capital
- Increase in assets with a corresponding increase in capital
- Decrease in assets with a corresponding decrease in capital
- Increase in liabilities and decrease in capital
- Increase and decrease in assets
Each of these transactions can be further explained as-
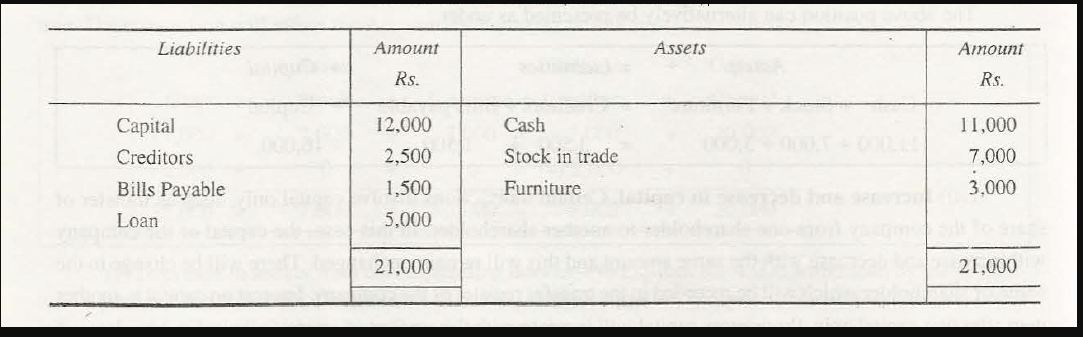
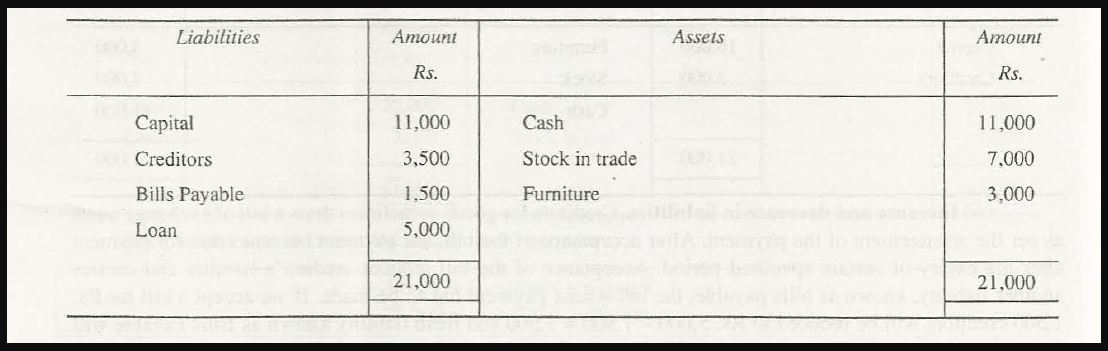
- Increase and decrease in liabilities
Various creditors of goods at times draw a bill of exchange in the company. This is based on the arrangement of payment. Once this bill is accepted, this payment becomes due for payment after a specific period’s expiry. The acceptance of this bill diminishes a creditor’s liability and creates another liability. The bill on which this payment needs to be made is known as bills payable.
- Increase in assets with a corresponding increase in liabilities
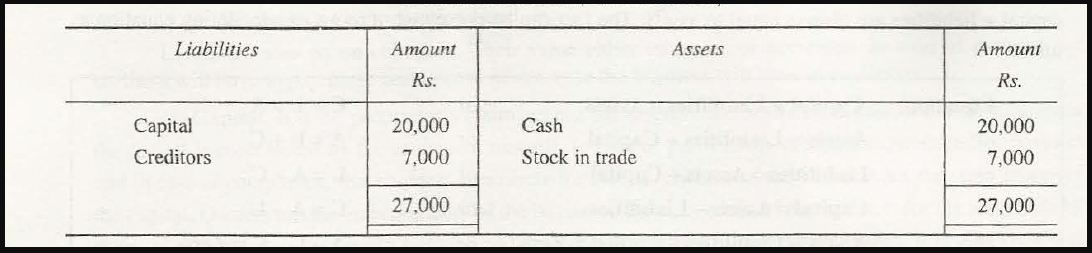
For example, if a business is started with an amount of $20,000, it will not only increase the assets, but even the capital of a firm will also be affected.
The financial position of a business will be affected by this transaction. This can be further explained as-
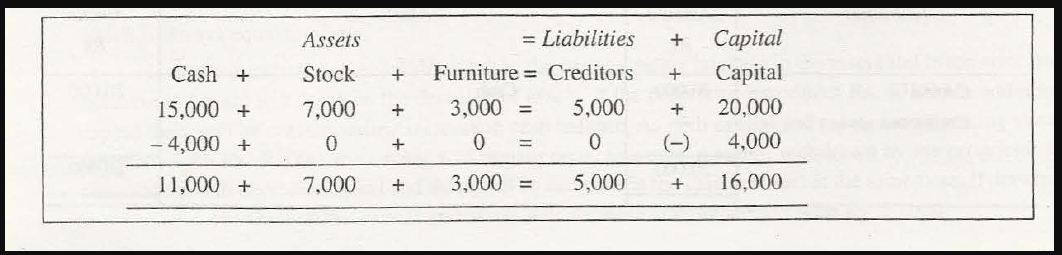
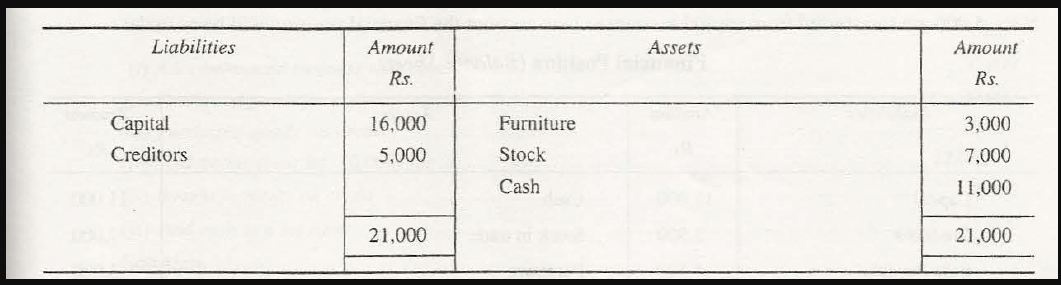
- Decrease in assets with a corresponding decrease in liabilities
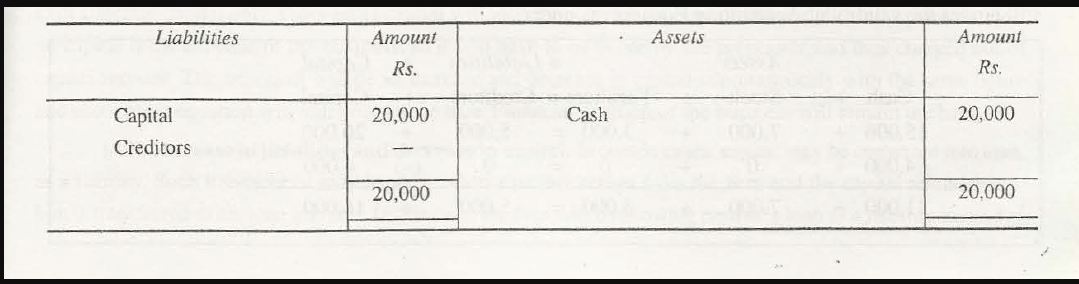
If a payment of $30,000 is made to the creditors, it will decrease creditors, liabilities of that company and even the value of assets will decrease. This decrease in assets and liabilities together at a time with the same amount will prove the Accounting equation to be true.
- Increase in capital and decrease in liabilities
When a loan is converted into capital, on the one hand, it lowers the liability of a business and on the other hand; it increases the business capital.
- Increase and decrease in capital
There are some business transactions which involve capital like transfer of company’s share from one shareholder to another. During such a time, a company’s capital will increase and even decrease with the same amount and this will be left unchanged. With the amount of interest allowed, the owner’s capital will increase.
- Increase in assets with a corresponding increase in capital
For instance, if goods are purchased on credit for an amount of $ 7,000, it will lead to an increase in the stock of goods with $7000. Further, it will even increase the liabilities of creditors. The financial position of this company will be affected as-
- Decrease in assets with a corresponding decrease in capital
The amount withdrawn by an owner for his personal use will automatically lead to a decrease in cash and capital.
- Increase in liabilities and decrease in capital
There are times when capital can be easily converted into a loan in the form of a liability. Such transactions occur when associate retires from a company and the capital which was refundable to him get transferred to his loan account. In such cases, instead of his capital, the company will show its partner’s loan as a liability. This leads to an increase in liabilities and an automatic decrease in capital.
- Increase and decrease in assets
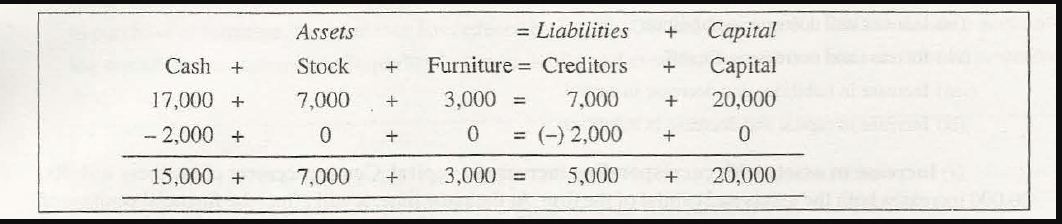
A purchase of furniture involves both the assets- cash and furniture. This will lead to a transaction where furniture will increase as an asset and then get decreased as cash. Even an increase in an asset with the same value will not affect the accounting equation.
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Meaning of gaap
- Origin of transaction
- Book keeping
- Source documents or vouchers
- Accounting voucher and its types
- Accounting equation
- Analysis of transactions
Links of Next Accounting Topics:-
- The concept of debit and credit
- Subsidiary books or sub division of journal
- Balancing of ledger accounts
- Meaning of trial balance
- Balance sheet in final accounts without adjustments
- Adjustments additional information in preparation of final accounts
- Meaning of bank reconciliation statements
- Bills of exchange concept of bills of exchange
- Errors affecting or disclosed by trial balance introducing the concept
- Meaning of depreciation