The three accounting terms like that of- assets, liabilities and capital, are regarded as the constituents of business transactions. Not only are these terms inter-woven, but inter-related too. However, these terms can be further explained.
- Assets
Assets signify the total valuable things which are owned by a company. The expenses borne by a company for acquiring these valuable resources in its business are also known as assets. These assets are a form of one-time investments with a prolonged future usage. These assets are in no ways meant for sale. Further, these assets play an important role in the profit earning capabilities of a company.
There are various assets like-
- Cash at bank
- Cash in hand
- Investments
- Plant and machinery
- Goodwill
- Land and Building
- Furniture and fittings
- Book Debts or Sundry Debtors
- Closing Stock
- Tools and Equipment
- Patents, trademarks, etc.
- Bills Receivable
- Accrued Income
- Prepaid Expenses
- Liabilities
Claim put up by proprietors and creditors against various assets of a company are known as that organization’s liabilities. These liabilities are even known as claims or equities. Thus, the term liability can be defined as the claim put up by outsiders against a particular company like the creditors of various expenses and goods. It is the account of which an organization remains indebted for certain time duration to its investors and outside parties.
Some of these external liabilities are listed as follows-
- Creditors for goods
- Creditors for expenses
- Other liabilities.
These can be further explained as-
- Creditors for goods
- Bills payable
- Sundry creditors
- Creditors for expenses
- Unpaid Wages to Workers
- Outstanding salaries to employees
- Due rent left unpaid
- Other liabilities
- Overdraft or bank loan
- Debentures
- Partner’s loan
- Employees Provident Fund
- Loan from Financial Institution like IDBI, IFC, etc.
- Workmen’s Compensation Fund
The liabilities of a business organization keep on changing. The values of these liabilities continue increasing or decreasing. In case, of an increase in liability, that company needs to pay more while in the case of a decrease, the company has to pay a lesser amount.
- Capital
Capital means a proprietor’s monetary entitlement against the various assets of his company. When the business is run by one owner, the whole capital needs to be contributed by him only. However, if a business is a partnership, its capital is funded by its partners. In the case of companies, it is the shareholders who contribute for the company’s capital.
Not only do these owners act as entrepreneurs of their business, but they are even the sponsors of the business capital. In return, they get profits for the risk taken in their business. If a particular amount of profit remains undivided or kept aside as funds and reserves, it is even known as the owner’s claim. This claim of the proprietor can be described as under-
- Capital
- Interest on Capital
- Profit or retained earnings
- Reserve fund, general reserves
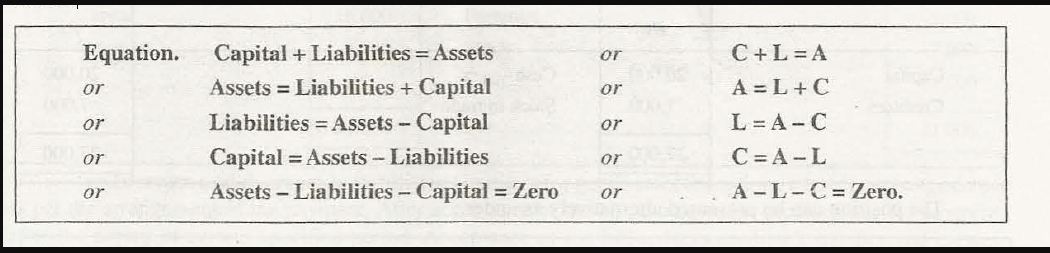
Accounting Equation
Description
The business transactions of a company are always financial in nature. Thus, every business transaction of an organization affects the financial position of that business. Each of these transactions either decreases or increases the assets, the liabilities or the capital. Each business has got certain assets of its own. These assets are bought with the capitals which have been supplied to the company by its owners or creditors. No matter in which form the funds of creditors and owners are in, they build up assets of a company.
For instance, if a company receives $ 2,00,000 as its capital from the owner and then retains the amount in the firm, it will form to be an asset of- ‘cash in hand.’ Among this, if $50,000 is deposited in the bank, then the capital structure will be divided. The total capital of this firm will be denoted by two assets like-
- Cash in hand of $ 1,50,000 (a sum of $50,000 being deposited at the bank out of its entire capital of $ 2,00,000.)
- Cash at bank of $50,000
If this company now purchases furniture of $ 20,000 and pays it from that cash deposited at the bank, then its capital structure will again change. It will be like-
- Cash in hand of $ 1,50,000 (a sum of $50,000 being deposited at the bank out of its entire capital of $ 2,00,000.)
- Cash at the bank of $ 30,000 (since furniture worth of $20,000 was bought, its bank balance has come down by $20,000.)
- Furniture of $ 20,000
Accounting equations are a declaration of equality between a company’s total debits and credits. With the example depicted above, it can be stated that the capital of a company is always equal to its assets.
An increase in capital will automatically lead to an increase in the value of assets of a company. Similarly, a decrease in the value of capital will decrease the value of these assets. If the owner withdraws money for his personal use, that results in a decrease in assets’ value. For example, if he withdraws a sum of $10,000 from the cash at bank or reserves, then the valuation of his company’s assets will also decrease by $10,000.
Liability of creditors in Accounting Equations
It is widely accepted that a business does not have any asset or liability or capital of its own. The business receives sponsor ships from its owners and creditors. It keeps these in the form of several assets. This justifies that liabilities + capital is always equal to that of its assets. This can be denoted in the form of accounting equation as follows-
Links of Previous Main Topic:-
- Book keeping
- Meaning of gaap
- Origin of transaction
- Origin of transaction
- Source documents or vouchers
- Accounting voucher and its types
- Accounting equation
Link of Next Accounting Topics:-
- Computation classification of transactions
- Balancing of ledger accounts
- Meaning of trial balance
- Balance sheet in final accounts without adjustments
- Adjustments additional information in preparation of final accounts
- Meaning of bank reconciliation statements
- Bills of exchange concept of bills of exchange
- Errors affecting or disclosed by trial balance introducing the concept
- Meaning of depreciation